Hreflang tags and language detection are the two main multilingual SEO strategies. Both are designed to help search engines display users the most appropriate language version. However, while the goal is the same, the way they work and their impact on SEO can be very different, and choosing the wrong approach can cost your website international traffic.
This article compares hreflang and language detection, covering their definitions, advantages, disadvantages, and technical tips for proper implementation. If you’re unsure which one to use, don’t worry—there’s a handy guide at the end to help you determine the best strategy for your website’s needs.
What are the hreflang tags?
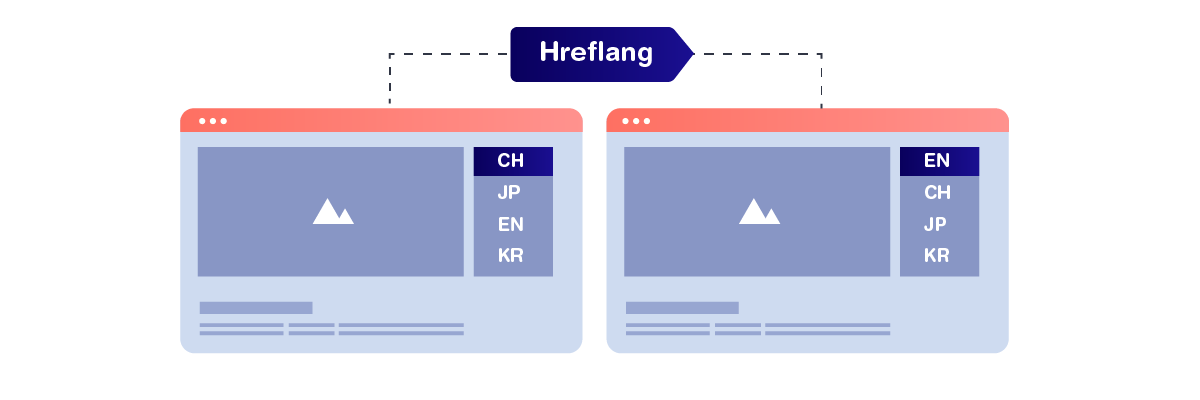
Hreflang tags are HTML attributes that tell search engines about a web page’s language and geographic region versions. These tags are especially useful for multilingual websites because they help Google and other search engines show users the most relevant version of a page based on the language they speak or their location. So, you have a page with the same content but translated into multiple languages or aimed at different countries. In that case, hreflang can prevent duplicate content and ensure visitors are directed to the most appropriate version.
Here’s an example of using hreflang in HTML:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://www.yourweb.com/en-us/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr-fr" href="https://www.yourweb.com/fr-fr/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="de-de" href="https://www.yourweb.com/de-de/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://www.yourweb.com/" />
Explanation:
- hreflang=”en-us” indicates that the page is intended for English speakers in the United States.
- hreflang=”fr-fr” for French speakers in France.
- hreflang=”de-de” for German speakers in Germany.
- hreflang=”x-default” is used for the default page if no language version matches the user’s preferences.
In addition to being included in the <head> element, hreflang can be added via HTTP header or XML sitemap, which is especially useful if you use a CMS or manage multiple pages. In a sitemap, you can list all page versions using a format like this:
<url>
<loc>https://www.yourweb.com/</loc>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://www.yourweb.com/en/" />
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="https://www.yourweb.com/es/" />
</url>
Using hreflang correctly can help improve user experience, prevent confusion due to inappropriate language display, and strengthen your international SEO strategy.
What is language detection?

Language detection automatically recognizes the language used in a text or web page. On websites, this is usually done through scripts or server configurations that read certain signals from the user as language settings in the browser or IP address to guess what language is best suited for display. This concept comes from Natural Language Processing (NLP), where language detection is considered part of the text classification process, aiming to identify the language before further processing accurately.
Language detection is often used to improve user experience automatically. For example, when you visit a global website and are immediately redirected to the Indonesian version simply because your browser is set to Bahasa Indonesia, language detection is usually done by reading the browser’s accept-language header, which lists the user’s preferred languages.
While practical, this approach can be problematic if the system detects the wrong language or doesn’t allow the user to change the language manually.
Pros and cons of hreflang tags vs language detection
Regarding SEO optimization for multilingual sites, the two main strategies often compared are hreflang tags and language detection.
Before you determine which method works best for your site, it’s important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. Below, we will discuss in detail how hreflang works and the pros and cons of both.
Hreflang tags
The following are some of the pros and cons of using hreflang tags.
Pros
- More accurate language and location targeting: With hreflang, you can show search engines which language and region versions are relevant for each page. For example, a page with the tag hreflang=”en-us” will be displayed for users in the United States, while hreflang=”en-gb” is intended for the United Kingdom. This helps ensure users find the version of the page that best suits their preferences.
- Prevents duplicate content issues: Google understands that pages with hreflang are translated versions of each other, not copied content. This avoids duplicate content penalties in SEO and helps each version of the page rank in its target market without competing with each other.
- Compatible with multiple languages and regional versions: Hreflang can be used for language differences and regional variations within the same language. For example, you can have German versions for Germany (de-de) and Switzerland (de-ch), allowing for more detailed content personalization for each market.
Cons
- Implementation complexity: One of the biggest challenges is the tag structure, which must be very precise. You must ensure that all pages reference each other using hreflang, including references to the page (self-referencing). This can be especially tricky for large-scale sites.
- Prone to technical errors: Errors such as incorrect language or region codes, inconsistent links, or poor sitemap structure can cause search engines to ignore hreflang completely. If not checked regularly with tools like Google Search Console or hreflang validation tools, this can damage international SEO strategies.
- Not fully supported by all search engines: While Google supports hreflang well, Bing does not officially recognize it. This means the effect is greater on Google and doesn’t necessarily guarantee a consistent experience on other search engines.
Language detection

The following are some of the pros and cons of using language detection.
Pros
- A more practical user experience: By automatically detecting the user’s language (e.g., via browser headers or IP address), the site can instantly display the most relevant content version without manually selecting it. This makes the access process faster and more convenient, especially for first visits.
- Flexible and customizable: Language detection can be used alongside technologies such as cookies or local storage to store user preferences. This means that users will not have to reset the language when they return to the site. This can increase loyalty and convenience in the long run.
- Useful for global content without separate URL structures: If your site doesn’t already use different URL structures for each language, language detection can be a temporary solution to still serve relevant content to a wide range of users without major technical changes.
Cons
- Less SEO-friendly – Automatic redirects based on language detection can confuse search engine crawlers like Googlebot, which may be unable to access other page versions. This can leave pages in different languages poorly indexed, lowering your visibility internationally.
- Lack of transparency for users – If users are not given the option to select or switch languages manually, they can get stuck on the wrong version, for example, when traveling and the browser language doesn’t match their preferences. This can create frustration and increase bounce rates.
- Not always accurate – Language detection relies on signals that can change or be inaccurate, such as browser settings or the user’s IP. For example, someone who speaks English but lives in Japan may be redirected to the Japanese version instead, even though they don’t understand the language.
Here’s a comparison table in English summarizing the pros and cons of hreflang tags vs language detection:
Feature | Hreflang tags | Language detection |
Accurate targeting | Allows precise targeting of both language and regional variations (e.g., en-us vs en-gb) | Automatically serves content based on the user’s browser or IP, offering quick access |
SEO benefit | Prevents duplicate content issues, helping SEO by clarifying translations to search engines | Can display relevant content without needing unique URLs or complex SEO setup |
Scalability | Supports multiple languages and regions with detailed personalization | It can be integrated with cookies or local storage to remember user preferences |
Implementation complexity | Requires exact tag setup and self-referencing across all page versions | Easier to set up but limited in terms of SEO optimization |
Error-prone | Vulnerable to technical issues (e.g., wrong codes, broken references), which can break functionality | Detection can misfire (e.g., based on wrong IP or browser setting), leading to poor UX |
Search engine result | Fully supported by Google but not by all search engines like Bing | Can confuse crawlers with automatic redirects, affecting SEO and indexing |
User control | No direct control for users—relies entirely on search engines to interpret tags | It may lack a manual language switch option, frustrating users if wrongly redirected |
Technical tips for hreflang and language detection
Here are some important technical tips you can apply when using hreflang tags and language detection in your multilingual SEO strategy.
Hreflang tags
Below are some tips that you can apply when using hreflang tags.
Use correct formatting

The hreflang format must comply with standards recognized by search engines like Google. The common format used is:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="xx-YY" href="https://example.com/page" />
Where xx represents the language code (e.g., en for English) and YY represents the country code (e.g., us for the United States). Using incorrect or inconsistent formatting can cause search engines to ignore the tags.
You can also use just the language code if you’re not targeting a specific region, such as hreflang=”es” for general Spanish content. However, adding a region code like es-mx (Spanish–Mexico) can be more effective for targeted strategies. Ensure that all tags are neatly written and placed in the <head> of the page, in the HTTP header, or in an XML sitemap.
Always include self-referencing tags
One common mistake is forgetting to include a self-referencing tag—this means the page must also reference itself using an hreflang tag. For example, if you have the page example.com/en-us, that page must also contain:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://example.com/en-us" />
This is crucial because Google uses it to confirm that the page is part of a multilingual version network. Without it, the hreflang tags may not function correctly and can confuse search engine crawlers when indexing the appropriate version of a page.
Avoid inconsistencies between pages

Each page within an hreflang network must consistently reference its language variants. That means if Page A references Page B as the fr-fr version, then Page B must also reference Page A as the en-us version (or whichever language it represents).
Inconsistencies are common in large websites with many pages, and if considered erroneous, they can cause search engines to disregard all tags. Ensure every page correctly references its counterparts using a complete and consistent hreflang structure.
Use sitemaps for large-scale
For large websites with multiple language versions and numerous pages, manually adding hreflang tags to HTML can be overwhelming. In this case, an XML sitemap is a practical alternative to defining the hreflang relationships between pages.
Google supports hreflang implementation via sitemaps, a more efficient way to manage multilingual SEO. It reduces the risk of technical errors and simplifies maintenance. Follow the correct XML format and update the sitemap regularly when pages are modified, or new languages are added.
Validate with tools

Once implementation is complete, you must validate all hreflang tags using tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog. These tools help detect incorrect codes, inaccessible pages, or incomplete relationships.
Validation shouldn’t be a one-time task. Perform it regularly—because even small errors, like extra space in a URL or a deleted page still referenced by an hreflang tag, can significantly affect your international SEO performance.
Language detection
Below are some tips that you can apply when using language detection.
Use language default with manual option
While automatically detecting a user’s language is convenient, always provide a manual option so users can choose their preferred language. For instance, a user might be traveling in another country or using a browser set to a language they don’t understand.
By offering a visible button or language selection menu, you give users control over their experience. This also helps prevent frustration when language detection is inaccurate, and users can’t easily find a way to switch the site’s language.
Detection based on accept-language header
One of the most accurate methods of detecting a user’s language is reading the browser’s Accept-Language header. This header indicates the user’s language preferences, such as en-US, id-ID, or fr-FR, and is sent with every request to the server.
This method is typically more reliable than IP address-based detection, as browser language settings better reflect personal preferences. However, avoid automatically redirecting users without allowing them to choose a different version.
Avoid automatic redirects without fallback
Automatically redirecting users to a specific language version can enhance user experience and cause major issues if no fallback is provided. For example, users may get stuck on a page they can’t understand and have no clear way to switch back.
From an SEO perspective, auto-redirects can also prevent Googlebot from indexing alternative language versions. A better solution is to show a suggested language notification—such as a pop-up or banner—and offer users the choice to stay on the current page or switch to another language version.
Use cookies or local storage

Once a user selects their preferred language, you can store that preference using cookies or local storage in the browser. This allows your site to display the chosen language automatically on future visits.
This method is user-friendly because it prevents users from having to reselect their preferences every time. However, don’t rely solely on cookies for detection—always include manual options to keep the user experience flexible.
Consider using a service like Linguise to simplify multilingual content implementation and management. Linguise automatically applies real-time translation systems, fully supports hreflang and language detection, and provides complete control over multilingual SEO—without the need for complex manual configurations.
Which one should you choose for multilingual SEO?

Choosing between hreflang tags and language detection depends on how your site is structured and what kind of experience you want to give your users. Both have different functions but can complement each other if applied correctly.
Use hreflang tags when:
- You want to signal search engines which version of a page is most relevant based on the user’s language or location.
- Your site has separate pages for each language or region (e.g. example.com/en-us/ and example.com/fr-fr/).
- You need an SEO-friendly solution that helps avoid duplicate content issues between language/region versions.
Meanwhile, use language detection when:
- You want to automatically adjust the language based on the user’s browser settings.
- Your site is dynamic or has a single domain that displays content in multiple languages without separating it into special URLs.
- You prioritize user experience by displaying the appropriate language at the start of the visit but still providing a manual option to change it.
You can also combine the two, using hreflang for search engine guidance and language detection to provide a comfortable experience for users at the beginning of their visit.
Conclusion
Choosing between hreflang tags and language detection in your multilingual SEO strategy depends on your site’s needs and structure. Hreflang offers more accurate control over the language and region versions displayed by search engines. However, its implementation can be complicated and prone to technical errors. Meanwhile, language detection is more practical and provides a fast and automated user experience. However, it tends to be less SEO-friendly as it can confuse crawlers and reduce page visibility across different languages.
If you want optimal results, combining both can be the best approach for SEO purposes and language detection to enhance the user experience. To make it easier to implement both without the technical hassle, you can use Linguise. This platform can automatically apply hreflang tags without you needing to configure it. Try Linguise now and maximize your international traffic potential!