When managing a website and SEO, choosing to utilize subdomains or subdirectories for website structure is a widely discussed topic. Both subdomains and subdirectories offer unique benefits and consequences for SEO. Recognizing the variances between the two and determining the appropriate usage for each can significantly influence the effectiveness of your SEO strategies and the general performance of your website.
In terms of SEO, the objective is to enhance your website to achieve a higher ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). This includes boosting domain authority, improving user experience, and increasing organic traffic to your site. Your website setup, such as using subdomains or subdirectories, may influence these aspects.
We will explore subdomains and subdirectories, their impact on SEO, strategic use cases for each, best practices for implementation, and insights from Google’s perspective. This will help you better understand subdomains and subdirectories and equip you with SEO implementation tips to make informed decisions for your website. So, let’s dive in and explore subdomains and subdirectories!
What are website subdirectories and subdomains?
Website structures can be categorized into two main types: subdirectories and subdomains.
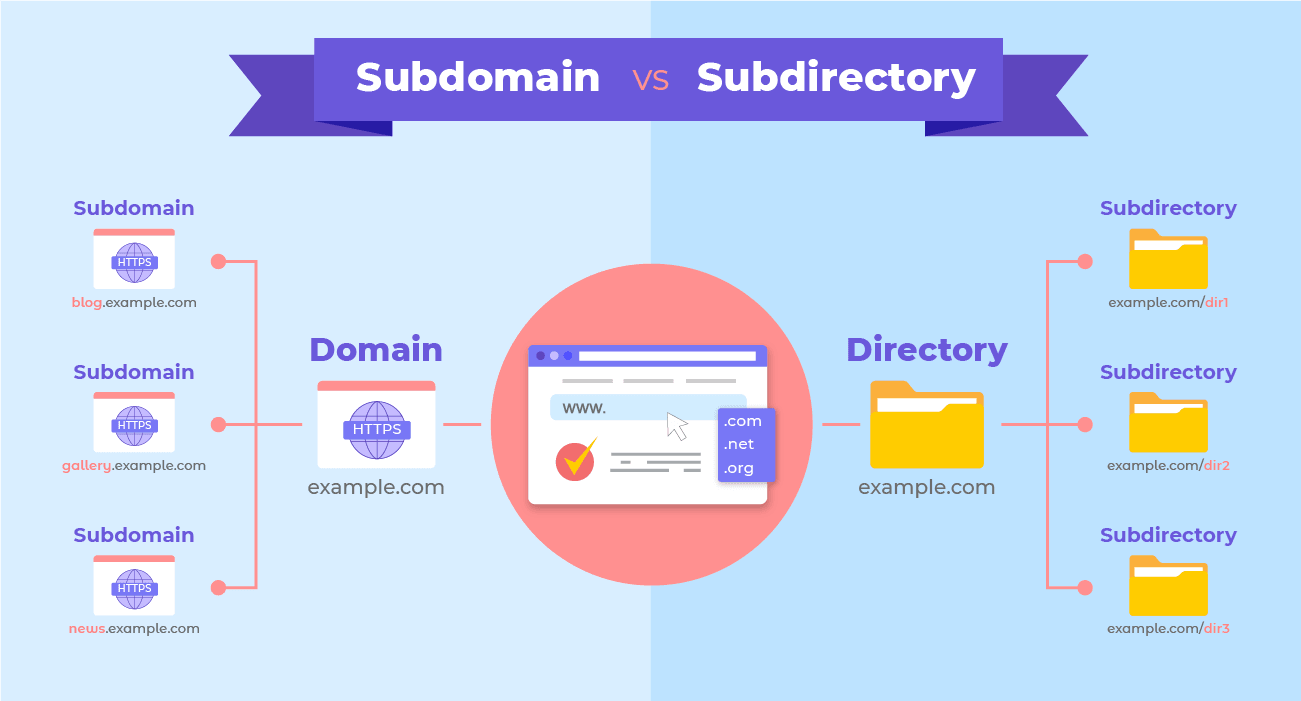
Subdirectories are content subfolders within a website’s main domain or root domain. They organize and categorize different sections of a website’s content. Subdirectories share the same main domain and have a URL structure that comes after the root domain. For example, a subdirectory for a website’s blog section could have a URL like “example.com/blog.”
On the other hand, subdomains are separate entities within a website with their own unique domain name. They are created by adding a prefix before the main domain in the URL. For example, a subdomain for a website’s support page could have a URL like “support.example.com.”
Subdirectories
Subdirectories are a commonly used website structure for organizing and categorizing content. They are subfolders that exist within the main domain or root domain of a website. Subdirectories allow you to create a clear hierarchy and structure for your website’s content.
The URL structure of subdirectories follows a consistent pattern, with the subdirectory name coming after the root domain. This makes it easy for users and search engines to navigate and understand the organization of your website. For example, if you have a blog section on your website, the URL for a blog post within that subdirectory would look like “example.com/blog/blog-post“.
One of the advantages of using subdirectories is that they share the same domain authority as the main domain. This means that any backlinks or authority gained by the subdirectory pages can contribute to the overall ranking of the main website. Subdirectories allow easy content management and updates, as everything is contained within a single domain.
Subdomains
Unlike subdirectories, subdomains are separate entities within a website with a unique domain name. They act as separate websites under the main domain, each with its own content, design, and functionality.
A subdomain’s URL structure differs from a subdirectory’s, as the subdomain name comes before the root domain. For example, a subdomain for a website’s blog section could have a URL like “blog.example.com.”
Subdomains are commonly used to create separate sections within a website that require distinct branding, content, or functionality. For example, an ecommerce website might have a subdomain for its online store, a subdomain for customer support, and a subdomain for its blog. Each of these subdomains can have its own unique design and content, tailored to its specific purpose.
It’s important to note that subdomains are treated as separate websites by search engines. This means that the authority and backlinks of the main website do not directly influence the subdomains, and vice versa. However, subdomains can still contribute to the overall visibility and SEO performance of the main website.
The impact of subdomains vs subdirectories on SEO
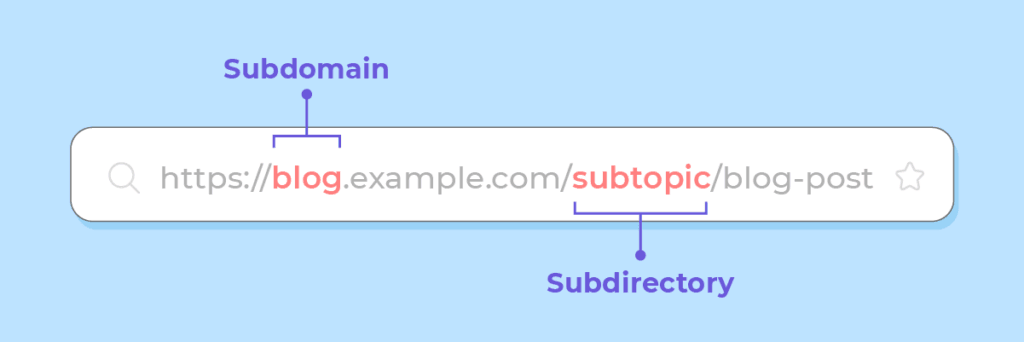
The choice between subdomains and subdirectories can significantly impact your website’s SEO. Understanding the implications of each structure can help you make informed decisions about optimizing your website for search engine visibility and rankings.
Search engine crawlers is essential in determining the visibility and ranking of web pages. As part of the main domain, search engine crawlers typically favor subdirectories as they are considered an integral part of the website. This means that the authority and backlinks of the main domain are shared with the subdirectory pages, which can positively impact their rankings.
Subdomains: Affect SEO and site authority
Subdomains have unique implications. While they offer the advantage of creating separate websites within a primary domain, they also have some considerations.
One key factor is that search engines treat subdomains as separate websites. This means that the authority and backlinks of the main site do not directly influence the subdomains and vice versa. Each subdomain is viewed as a separate entity with its domain authority.
This can be both a pro and a con. On one hand, subdomains allow for specialized branding, content, and functionality. They can target specific audiences and cater to your website’s different purposes, mainly when you target specific countries and implement international SEO.
On the other hand, subdomains require separate efforts to build authority and improve search engine rankings. It’s essential to carefully consider subdomains and ensure each subdomain serves a specific purpose that justifies the separate website structure.
Subdirectories: In SEO optimization
Subdirectories is essential in SEO optimization by providing a clear and organized structure for multilingual website content. They offer several advantages that can positively impact search engine rankings and user experience.
One of the key benefits of using subdirectories is that they share the same domain authority as the main website. This means that any backlinks or authority gained by the subdirectory pages contribute to the overall ranking of the main website. This can result in higher search engine rankings and increased visibility.
Subdirectories make content management and updates easier, as everything is contained within a single domain. The URL structure of subdirectories is also clear and easy to understand for both search engines and users. This can lead to higher click-through rates and improved user satisfaction.
Best practices use subdomains
Subdomains offer strategic advantages for specific use cases, allowing for brand diversification, separate sections, and targeting specific locations or audiences. Understanding these use cases can help you make informed decisions about implementing subdomains for your website.
One use case for subdomains is brand diversification. You can tailor each subdomain to its specific target audience and brand identity by creating separate subdomains for different product lines or brands. This can help differentiate your offerings and improve the user experience.
Brand diversification and targeting specific audiences
Using subdomains can be a smart move for businesses looking to offer different things to different people. Take “HomeEssentials,” a store that sells kitchen gadgets, electronics, and garden tools. They use subdomains like kitchen.homeessentials.com and electronics.homeessentials.com to separate their products. This way, they can make each section special for its shoppers with designs and deals that match what those customers want.
Subdomains allow businesses to expand to different areas without mixing everything up on one website. They make it easier to target specific groups or regions with content that speaks directly to them. It’s like having a special corner of your store for each product or customer type. Amazon is a good example of this. It uses subdomains to help ensure it can share targeted content and solutions based on its diverse user base.
For businesses operating in multiple countries or regions, subdomains can be useful for tailoring localization strategy content, language, and offerings to each specific market. For example, creating us.example.com for the United States and uk.example.com for the United Kingdom can improve user experience by presenting content in the relevant language and with market-specific offerings.
Display various types of content
Subdomains offer a strategic approach to managing and organizing a content-rich website, especially when it needs diverse categories or topics. By implementing subdomains, you essentially carve out dedicated spaces for each distinct type of content. This structure enhances the site’s overall organization and tailors the browsing experience to meet the specific needs and interests of different user segments.
If your website has lots of different information or areas—like help guides, community forums, and support sections—subdomains help keep everything tidy and easy to find.
- support.yourwebsite.com for help and support, where users can find answers and solutions.
- community.yourwebsite.com for your online community, where people can talk, share ideas, and help each other.
- guide.yourwebsite.com for guides and how-tos, where users can learn more about your products or services.
Think of each subdomain as its own mini-website that focuses on one specific thing. This setup makes it easier for your visitors to find exactly what they’re looking for. Plus, search engines like Google see each subdomain as its own site, which can help people find your content more easily when they’re searching online. It’s a win-win: your website is more organized, and your users get to where they want to go faster.
You need to do testing
Not only testing in translation websites but testing is also a crucial step to consider when deciding whether to use a subdomain or a subdirectory structure for your website. For example, let’s say you run an online store called “GadgetWorld” with a blog that provides the latest tech news.
You might be uncertain whether to place your blog under a subdomain (blog.gadgetworld.com) or a subdirectory (gadgetworld.com/blog). By conducting tests, you can gain valuable insights into how each structure affects your SEO results.
To perform this test, you can temporarily set up both versions and analyze metrics such as organic traffic, search rankings, and user experience. This practical approach allows you to determine which option—subdomain or subdirectory—best supports your SEO strategy. It might be the case that the blog under a subdomain starts ranking faster for tech news keywords because search engines treat it as a separate entity. Alternatively, the subdirectory version might benefit from the main site’s authority, improving the blog’s visibility in search results.
Best practices use subdirectories
It is important to plan carefully when creating subdirectories on your website, in order to maximize their impact on your site’s structure, search engine optimization (SEO), and user experience. Subdirectories are sections of your website that categorize and organize content under a broader directory. They can be very helpful in improving your website’s overall usability and visibility.
When setting up subdirectories, one key consideration is ensuring that they align with your website’s hierarchy and navigation structure. Organizing content into logical subcategories makes it easier for visitors to navigate your site and find relevant information efficiently. This not only improves the user experience but also signals to search engines like Google the relationship between different pages on your site.
Maintain a clear and logical site structure
Implementing subdirectories offers a chance to organize your website in a way that’s intuitive for both users and search engines. For instance, a well-structured e-commerce site might use subdirectories to categorize products, making it easier for shoppers to find what they’re looking for (e.g., yoursite.com/mens-clothing/shirts). This clarity not only improves user navigation but also aids search engines in understanding and indexing your content more effectively.
- Plan and organize your subdirectories based on logical categories or sections that align with your website’s content and purpose.
- Use clear and descriptive labels for your subdirectories to help users understand what each section represents.
- Ensure that your subdirectory pages are easily accessible through a clear navigation menu or sitemap. This can help users find the content they are looking for quickly and easily.
- Implement internal linking between subdirectory pages and other relevant pages on your website. This can improve navigation and help users discover related content.
- Regularly review and update your site architecture to ensure that it remains user-friendly and aligned with your website’s goals and objectives.
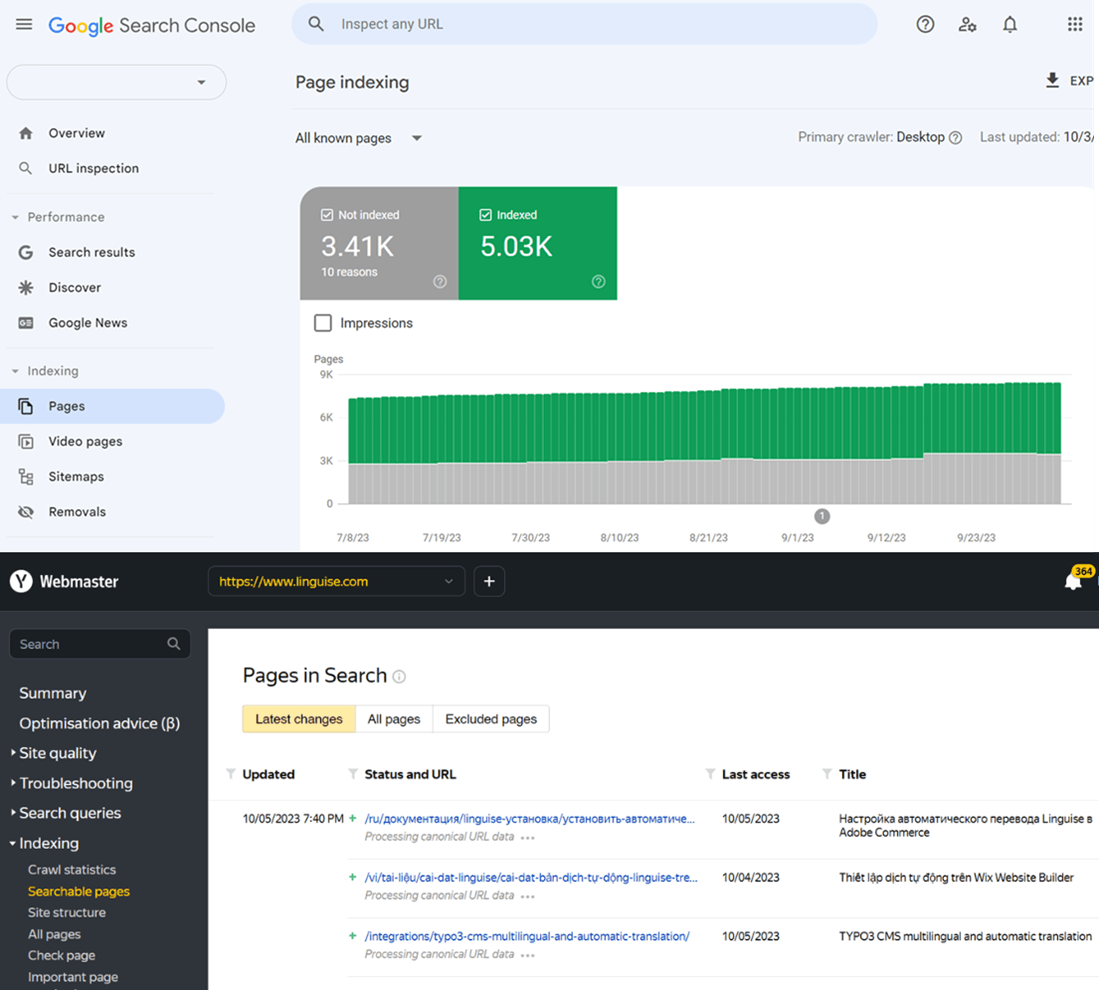
Simplifying content management and SEO tracking
Effective content management and SEO tracking are crucial for maintaining and optimizing your website’s performance. When implementing subdirectories, it’s important to simplify content management and SEO tracking processes. With all your content under one roof, so to speak, you can have a holistic view of your site’s performance in analytics tools like Google Analytics without the need to segment or aggregate data across different properties. This simplification can lead to more coherent and efficient analysis and decision-making processes. It allows for easier comparison of content performance across different sections of your site, enabling you to identify trends, issues, and opportunities more readily. This integrated perspective is invaluable for making strategic adjustments to improve your site’s engagement, SEO, and conversion rates.
Here are some tips for simplifying content management and SEO tracking when using subdirectories:
- Use a content management system (CMS) that allows for easy creation, organization, and publishing of content across subdirectories. This can streamline content management and ensure consistency.
- Implement a robust SEO tracking and analytics tool, such as Google Analytics, to monitor the performance of your subdirectories. Set up separate tracking codes or properties for each subdirectory to accurately measure their impact on SEO.
- Regularly review and analyze the performance of your subdirectories using the data provided by your SEO tracking tool. Monitor metrics such as search rankings, organic traffic, user engagement, and conversion rates to identify areas for improvement.
- Implement best practices for on-page SEO, including keyword optimization, meta tags, and internal linking, across all subdirectories. This can help improve search engine rankings and visibility for your subdirectory pages.
Insights from Google's Webmaster Guidelines
To gain insights into the impact of subdomains and subdirectories on SEO, it’s important to consider Google’s perspective. John Mueller, a search advocate for Google, has provided valuable insights on this topic.
In a video, Mueller states that Google’s algorithms do not prefer subdomains over subdirectories (or vice versa) when ranking web pages. He emphasizes that Google Web Search is fine with using either subdomains or subdirectories and that webmasters should use what works best for their setup and longer-term plans.
This means that from Google’s perspective, the choice between subdomains and subdirectories does not directly impact a website’s ranking. However, different website structures have their own advantages and considerations when it comes to SEO.
While Google’s algorithms do not favor subdomains over subdirectories (or vice versa), it’s important to follow Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to ensure your website is optimized for search engine visibility and rankings.
Google’s Webmaster Guidelines provide best practices for creating websites that are user-friendly and accessible to search engines. Key considerations include:
- Create a logical and organized website structure that is easy for users and search engines to navigate.
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich URLs that reflect the content of your pages.
- Optimize your website for mobile devices to provide a seamless user experience across different devices.
- Focus on creating high-quality and unique content that adds value to your users.
- Follow SEO best practices, such as optimizing meta tags, headings, and image alt text.
- Ensure your website is fast and has good performance to enhance user experience.
How to choose between subdomains vs subdirectories for your multilingual website?
Choosing the right structure for your multilingual website often boils down to a preference between subdomains and subdirectories, though many prefer subdirectories.
Here’s why subdirectories might be the better choice:
- Your site’s multilingual versions gain from your main domain’s authority, potentially improving their search engine rankings.
- The process is hassle-free, requiring no extra steps in your hosting setup.
- Tailoring your content for different languages is straightforward, with the option to use language-specific URL paths, like yoursite.com for English and yoursite.com/es for Spanish versions.
- Organizing each language version in separate subfolders simplifies navigation for both search engines and visitors.
In certain situations, using subdomains may be the better choice. For example, using a subdomain does not affect the crawl budget on the original sites, which is suitable for you to managed large multilingual sites in various languages.
Although additional setup steps are involved, subdomains offer greater technical flexibility.
Also, consider technical factors impacting your website’s performance and user experience. Here are some technical considerations to keep in mind:
- SSL certificates: Ensure that your website has the necessary SSL certificates to secure both the main domain and any subdomains.
- Website load times: Subdomains and subdirectories can affect website load times. Consider the impact on server resources and optimize performance accordingly.
- Server configuration: Check that your server configuration allows for the setup and management of subdomains or subdirectories. Ensure that the server can handle the increased load and traffic associated with the chosen structure.
Ready to create multilingual website?
After learning to choose between subdomains and subfolders for your site, you are ready to launch your multilingual website. Regardless of the subdirectory or subdomain you choose, Linguise, the best automatic plugin translation will help you manage multiple SEOs and make it easier to manage.
- Fully Compatible with Major Search Engines: Our system has been tested for maximum compatibility and effectiveness with all major search engines’ webmaster tools.
- Automated Multilingual Sitemap Generation and Updates: Keep your site structure clear for search engines in every language with automated sitemap functionality.
- Front-End Editing of Page Titles and Meta : Easily edit and optimize your page titles and meta descriptions directly from the front-end for each language, enhancing your SEO efforts.
- Canonical Tags for Multilingual Pages: Efficiently manage canonical tags for multilingual content, preventing duplicate content issues and strengthening your SEO.