When creating a multilingual website, language and locale are often used interchangeably or even simultaneously. Building a multilingual site is usually referred to as simply translating site content into various languages.
However, site localization is also happening within it. “Language” used on the site will differ from “locale” or the localization of site content.
“Language” merely translates content according to context into various languages. Meanwhile, “locale” is more specific than language, adapting to local user preferences such as formatting, dates, etc.
For those who still don’t understand the difference between language vs locale, let’s continue reading this article until the end!
What is the locale?
Locale is all website content, pages, formats, and settings that have been specifically tailored to suit individuals viewing the website in a particular country.
Localization involves cultural adaptation and adjusting your content for specific audiences in other countries. It goes beyond simply translating website content into another language. Localizing content means considering customs, technical formats, norms, and communication styles.
For example, when accessing the Airbnb site, the currency format displayed is Rupiah, which reflects the Indonesian currency, because the user is in Indonesia at that time.
Despite using the Rupiah currency, the language presented only remains in English if you manually change it to various desired languages.
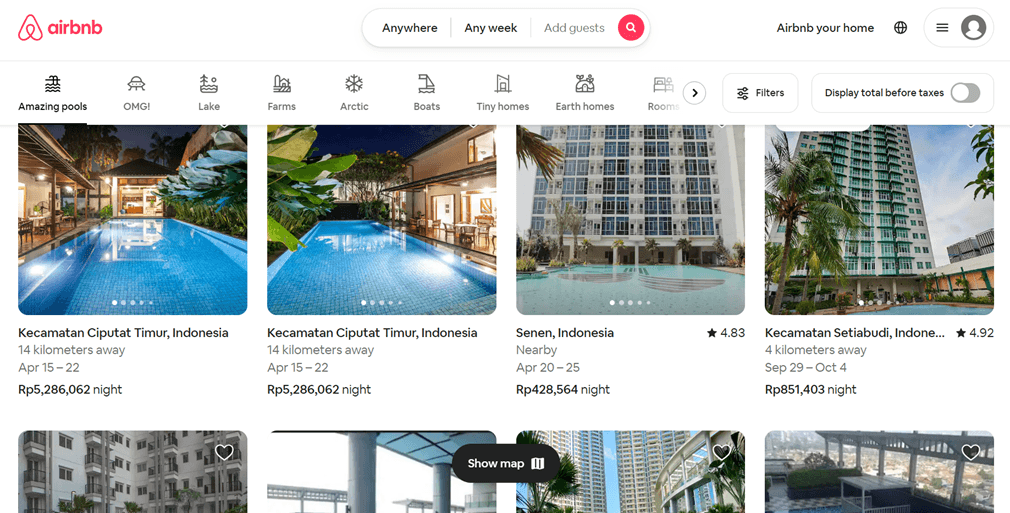
That’s correct. Localizing a website does indeed involve adjusting all content according to the language of the local user, but it can be different for some websites. Some websites often only localize important formats, such as currency, while still providing the option to switch languages.
Difference between language and locale
After understanding what locale is, then what is the difference between language and locale, especially in the context of a multilingual web? Below is a table of the differences.
No. | Language | Locale |
1. | Only related to text and grammar | Covers various aspects and custom settings (date format, currency, images, etc). |
2. | The main focus is translating content | Focus on adapting content as a whole according to local customs or culture |
3. | Usually, there is only 1 language option | Can have multiple locale variants in one language (e.g., en-US, en-GB, en-AU for English) |
4. | Language translation can be done without considering the locale | Content localization requires language translation and local adaptation |
5. | Ensure content is understandable to audiences in multiple languages. | Ensure the user experience is more familiar and in line with local preferences. |
Practically, you can create several versions of your site’s locale while keeping all content in just one language, such as English. This means that even though your main text content remains the same in English, you can customize other elements according to different locales.
For example, your e-commerce website targets users in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia. Although the product content, descriptions, and others are in English, you can:
- Use different date, time, and number formats (e.g., mm/dd/yyyy for the US, dd/mm/yyyy for the UK)
- Adjust currency (USD, GBP, AUD)
- Utilize appropriate abbreviations and measurements (e.g., feet vs. meters)
So, with the same English content, you can provide a more localized experience for visitors from different locations.
This approach is useful when translating all content into many languages is not feasible or cost-efficient. This light localization still helps improve engagement and conversions for your global audience.
Why should you differentiate between language and locale?
Why should you differentiate between language and locale? For businesses offering products or services to English-speaking audiences in various countries, you need to consider the differences in shipping processes and regulations in each country.
For instance, although audiences in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia all use the English language, the method of shipping goods to these countries may vary according to local rules and customs.
In this case, the business can simply create one version of the website in English. However, they need to provide three different local versions – for the US, UK, and Australia – to ensure that the shopping experience meets the expectations and cultures of each country.
Another scenario is when one location has several different languages in use. For example, in Switzerland, there are four official languages: German, French, Italian, and Romansh. A website serving the Swiss market should ideally offer options in all four languages.
Lastly, when a business wants to enter multiple locations simultaneously with different languages, for instance, a business aims to target English, French, and German-speaking audiences. For this, three versions of the website with other languages and localizations are required for each country.
So, separating language and localization management provides flexibility that can be tailored to the specific needs of audiences in each region, albeit with more efficient efforts.
What components are included in the locale?
In setting the locale, several vital components are typically considered and adjusted. Here are some you need to know:
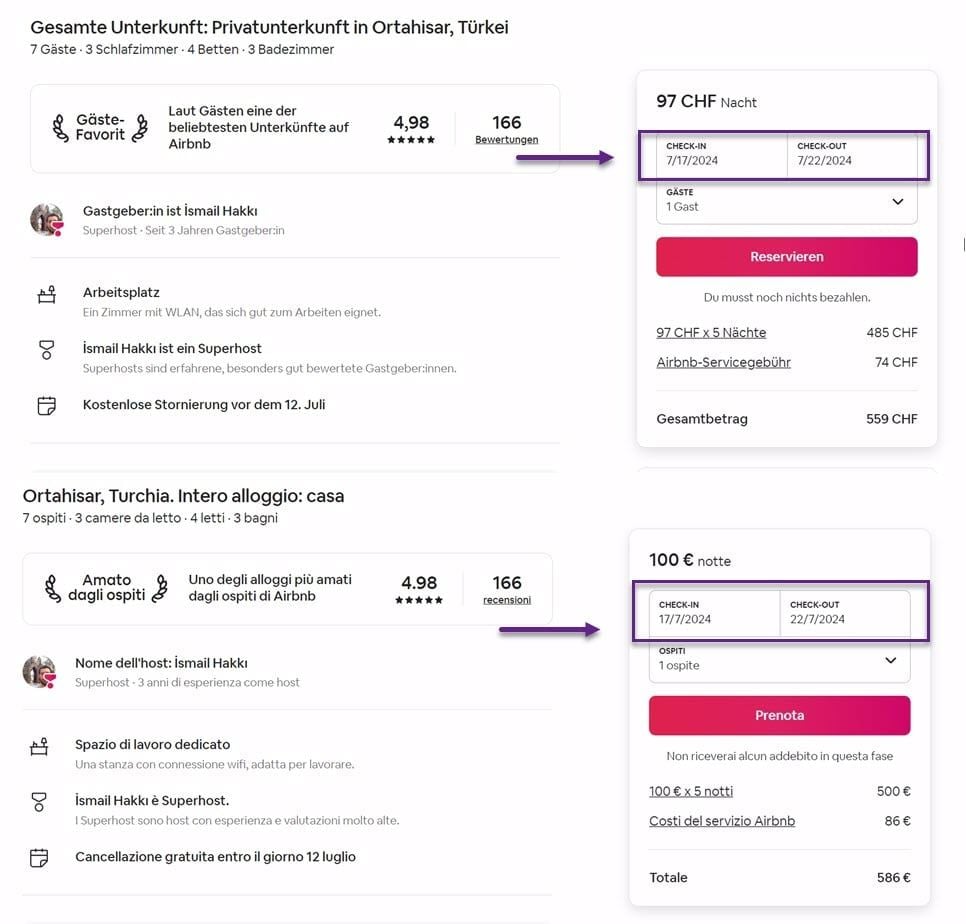
- Date, Time, and Telephone Number Formatting: Locale encompasses specific settings for the appearance and formatting of dates, times, and numbers according to conventions in a particular region or culture. For example, in the United States, the standard date format is mm/dd/yyyy (such as 05/21/2023), while in many European countries, it is dd/mm/yyyy (like 21/05/2023). Similarly, the telephone country codes differ, for instance, +44 for the UK and +1 for the US. Below are examples of the different date formats used. The first image is in Deutsch, while the second is in Italian.
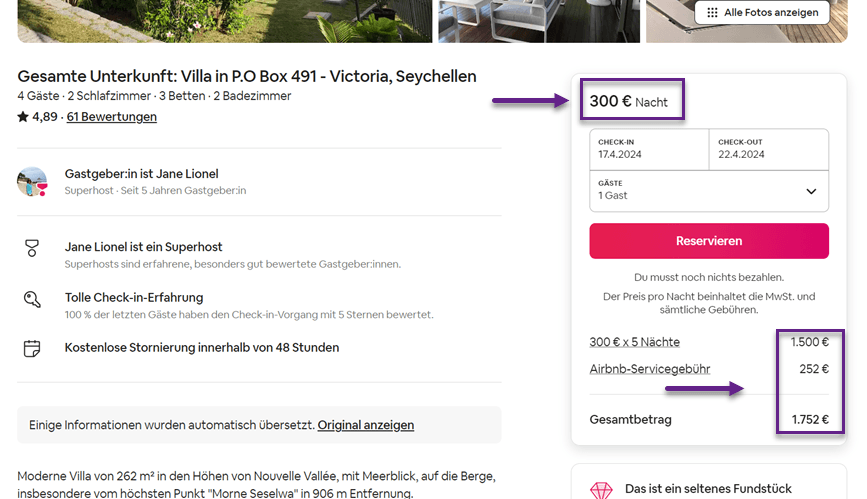
- Currency Settings: Locale also determines how currencies are presented, including currency symbols, symbol positions (whether before or after numeric value), thousands of separators, and the number of decimal digits displayed. For instance, in the United States, currency is displayed with the symbol $, like $25.99, whereas in Europe, the Euro currency uses the symbol €, such as €25,99.
- Shipping Options and Details: Locale plays a crucial role in presenting relevant shipping options and details to customers in a region. In the e-commerce industry, if you intend to ship to a specific country, you need to display specific shipping options for that country. For example, you wouldn’t want to list shipping companies that do not operate in the buyer’s country. This customization can be achieved through good localization. Additionally, you also need to adjust information such as estimated delivery times, shipping costs, and customs regulations according to the rules and practices in the destination country.
- Units of Measurement: Locale is essential in determining whether you will use imperial units (such as inches, pounds, or Fahrenheit) or metric units (such as centimeters, kilograms, or Celsius) in displaying product information. Some countries still use imperial units, while most others use the metric system.
- Local Regulations: In some cases, there may be countries that do not allow a product to enter their territory. For example, in streaming industries like Netflix, some shows or movies may not be available in certain countries. You can tailor your product or service offerings to comply with the regulations and preferences in each country.
How to setup the locale content on your website?
Now that you know what locale is and why it’s important for your business, how do you start localizing content on your website? Localized content can be achieved through automatic website translation services that also provide editing features and offer multiple languages.
The editing feature will assist you in localizing content to suit user preferences and local customs better. Meanwhile, having multiple languages readily available facilitates selecting the local language you wish to add.
Linguise translation service is one solution that can be used to set up locale content. It has several advantages that support locale content, such as a front-end live editor feature and providing more than 80 languages.
Without further ado, here are the steps:
Step 1 - Make sure your website is ready and has a Linguise account
Before starting, make sure your website is ready to be translated and localized. Apart from that, you must also have a Linguise account. If not, immediately register your Linguise account for free and enjoy a 30-day free trial.
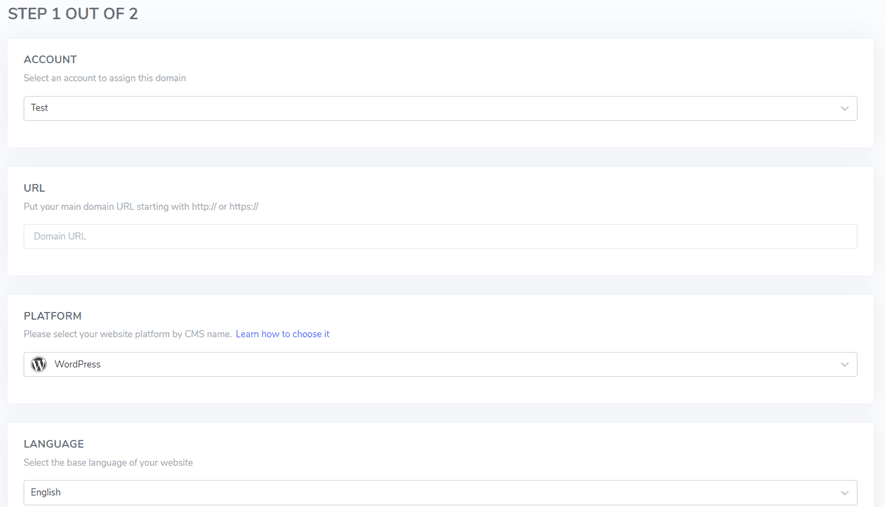
Step 2 - Add domain web and languages
Next, add the website domain and several languages you want. Some of the sections that you have to fill in include Platform, URL, Default Language, and Languages.
Step 3 - Install the Linguise plugin
Here, we will use WordPress as the platform. Therefore, you need to install the plugin translate WordPress, which is Linguise on your site. Click Plugins > Add New > search for Linguise > Install > Activate.
But don’t worry, if you don’t use WordPress. Because Linguise is integrate with more than 40+ CMS others.
Once downloaded, activate the API key that you got when adding the domain.
Step 4 - Set your locales
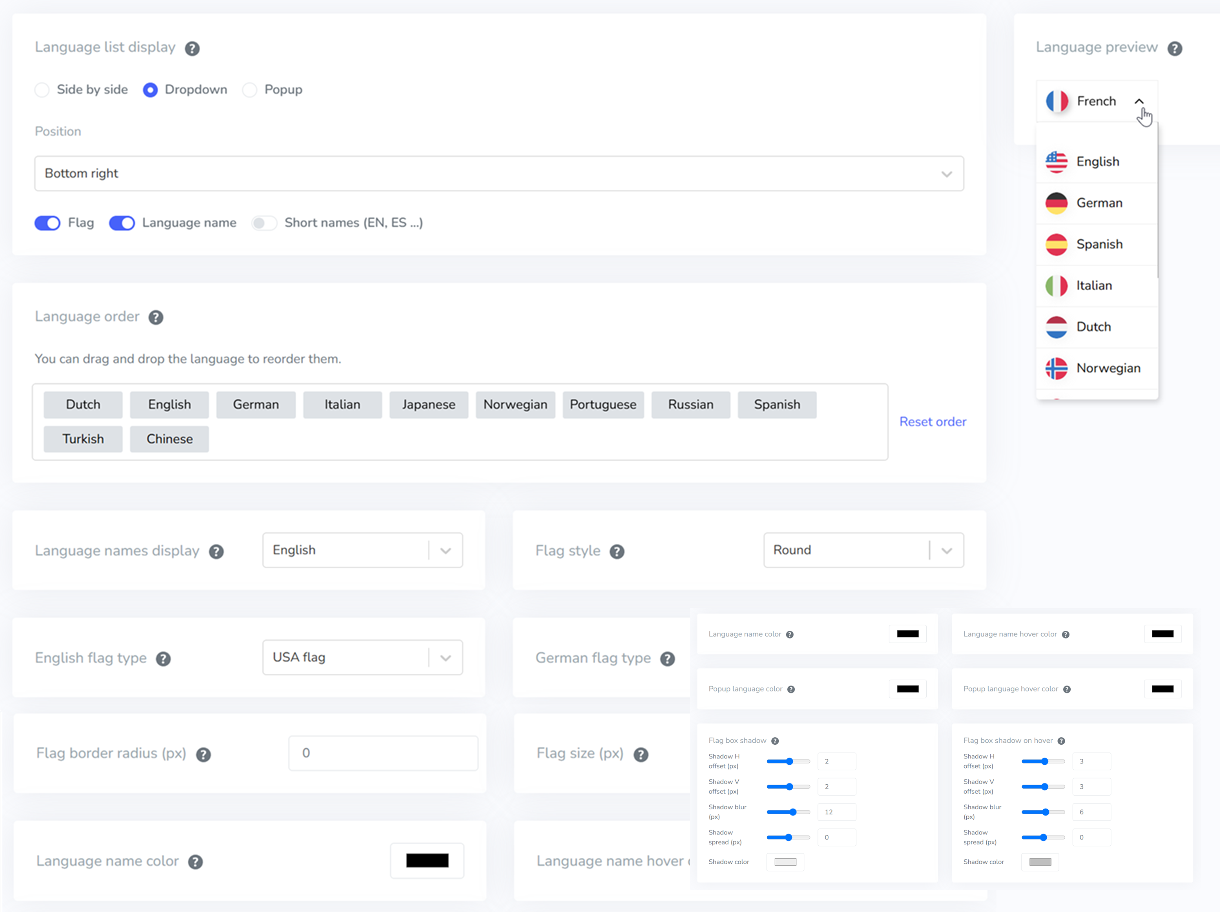
After successfully activating the API key, you will automatically receive a language switcher display according to the language you have chosen, whether it be a common language or for the locale.
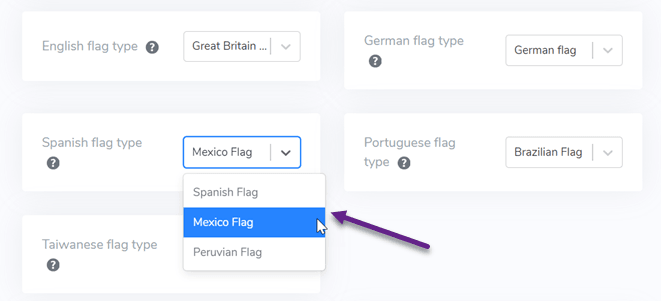
In the Linguise dashboard, there is a setting for language flags display, which includes displaying the language name. Here, you can customize the language display according to your needs.
For example, if you are targeting Mexico for your business, as we know, Mexico uses Spanish as its official language. Therefore, you can change the flag icon to the flag of Mexico but keep the language name as Spanish so that local users can easily recognize it.
Similarly, for the languages English, German, Portuguese, and Taiwanese.
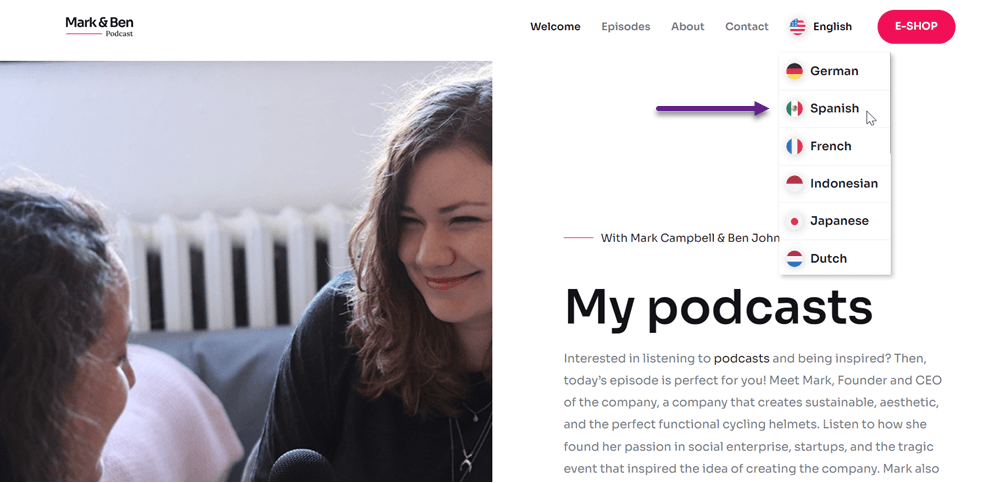
Apart from these settings, the language flag display also allows you to customize other rules, as in the display below.
Roughly, this is how the website appears after it has been configured, as described earlier.
Step 5 - Localize your content
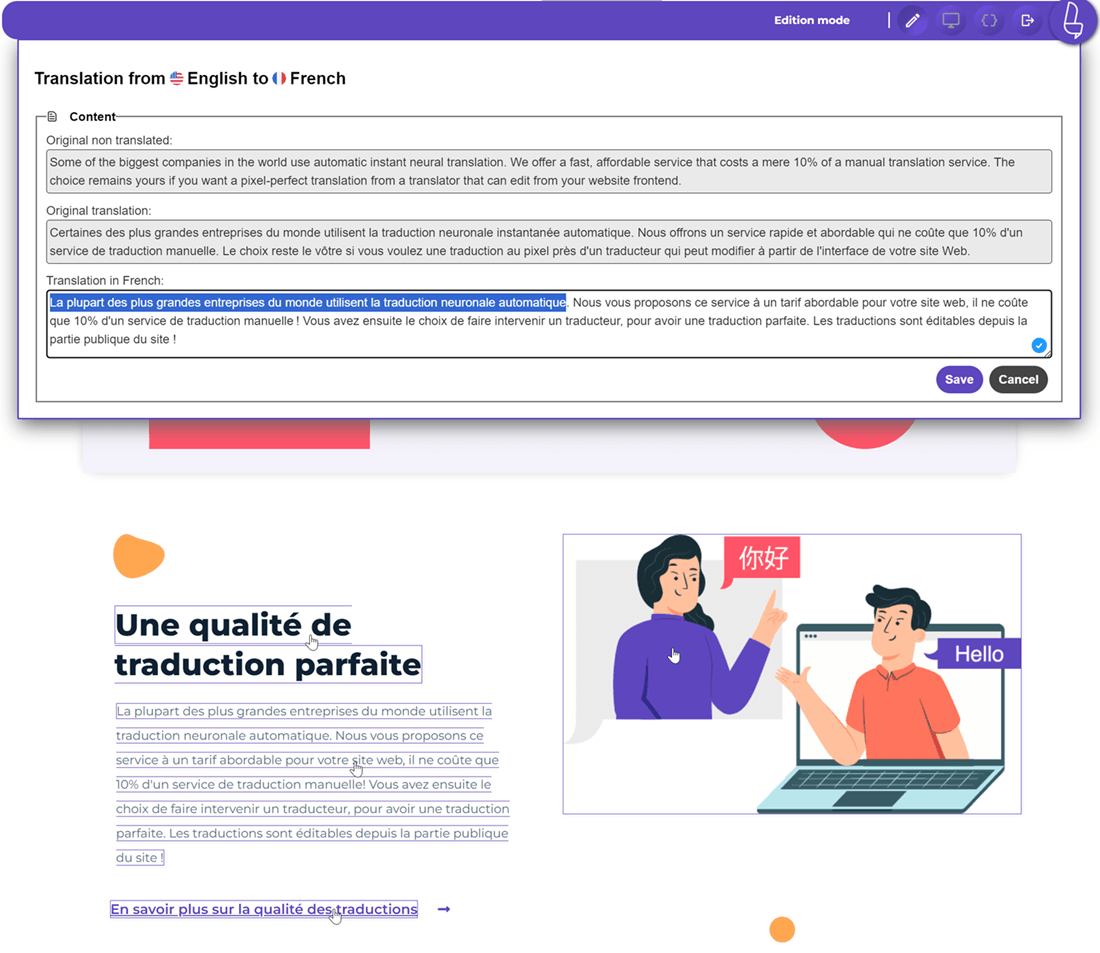
As explained above, several content components should be localized to align with the preferences of local users. With Linguise, you can localize content directly using the front-end live editor feature. To do this, open the Linguise dashboard and click on Live Editor.
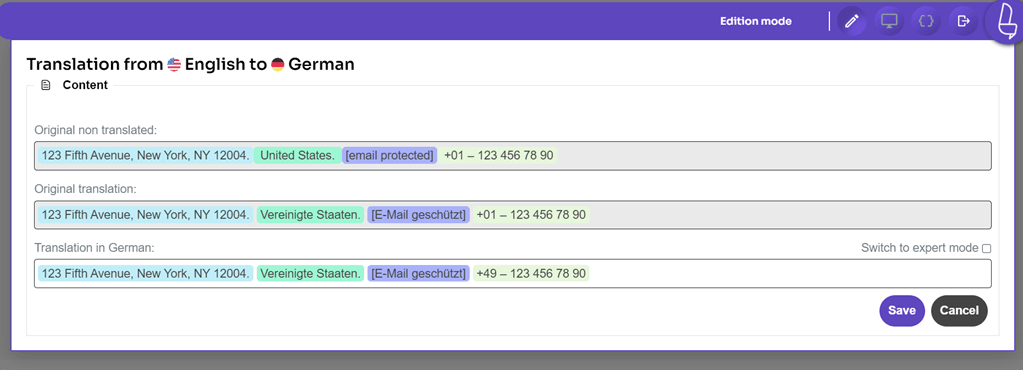
For example, as illustrated below, you can localize the telephone code, which initially is +1 for the US, to +49 when translated into German because the telephone code there is +49.
You can easily edit it by clicking on the part you wish to localize, entering the localized result as needed, and then clicking Save.
To learn more about content localization, you can read some of our articles.
Conclusion
Now you know what locale is and the difference between language and locale. When creating a multilingual website, it’s important to understand the distinction between language and locale. Language is only related to translating content into various languages. At the same time, locale encompasses adjusting various elements such as date, time, numbers, currency, shipping options, units of measurement, and local regulations to align with the preferences and culture of local users.
The key components in setting up a locale include the date, time, telephone number, currency, shipping options and details, units of measurement, and local regulations.
To manage locale content on a website, you can use automatic translation services that provide editing features and multiple language options, such as Linguise. Additionally, some other outstanding features supported by Linguise are:
- Translation rules (ignore text, exclude pages, etc).
- Perfect translation quality
- Multilingual SEO friendly
- Unlimited language addition
- Possible to add and setup access translators to collaborate
With Linguise, you can set up locale content on your website to better suit the needs of the local audience. So what are you waiting for? Sign up for a free Linguise account now and use the 30-day trial to translate up to 600 thousand words with unlimited languages!