Consumers are buying online now more than ever, and businesses need to increase their visibility in search engine results to be the buyer’s first pick. Recent statistics show that there are over 220 million online buyers in the US. The average spending for each of them in 2023 is expected to cross $5,300. Considering this, it can be said that businesses with more visibility will certainly make more profits.
Marketers worldwide use various search engine optimization (SEO) tactics to improve their rankings. However, using XML sitemaps is an approach that not many of them focus on simply because of a lack of knowledge or expertise. Using XML sitemaps helps search engines better understand your website and improve your ranking. However, it’s important to learn what an XML sitemap is prior to initiating the process.
Understanding XML sitemaps
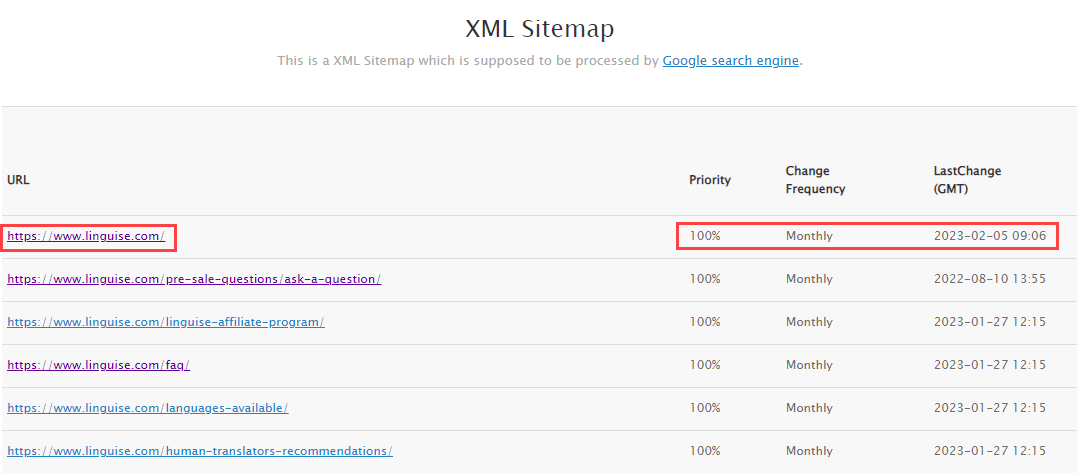
The structure for each entry on an XML sitemap is as follows:
- XML version declaration – includes details about the type of file crawlers are reading.
- URL set – provides search engines with details about URL protocols.
- URLs – includes a list of URLs for different pages of your website.
- Lastmod – provides details about when the most recent modifications to the file were made.
The difference between XML and HTML sitemaps
Not knowing the difference between an XML and a hypertext markup language (HTML) sitemap is quite common. As mentioned, an XML sitemap is used by search engines and crawlers. However, an HTML sitemap is used by actual website visitors. Where the XML sitemap allows search engines to understand the structure of your website, an HTML sitemap helps visitors navigate it.
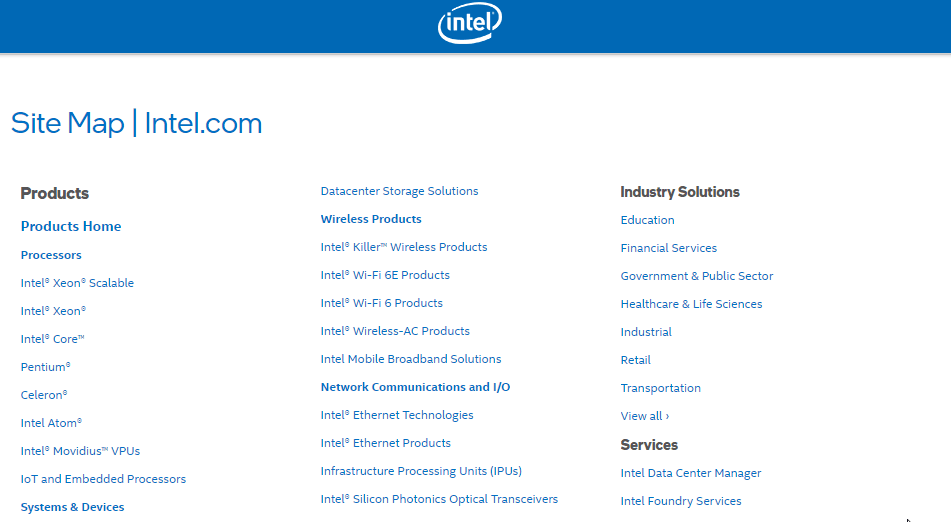
An HTML sitemap is a separate page on your website. It contains the names of the pages and subpages of your website. This means that in addition to having the product page, it will also have a list of all the products and their categories on your website. The names mentioned on the HTML sitemap have clickable hyperlinks. So if a visitor is having difficulties finding a specific page on your website, they can navigate to the HTML sitemap to locate and access it.
Where XML sitemaps help crawlers learn more about your website, and HTML sitemaps help you improve user experience. Most people often debate about one being better than the other; however, it’s important to understand that both should be used on a website. Where one helps improve technical aspects, the other focuses on the human element, and using both helps improve your search results rankings.
Here’s an HTML sitemap :
Translated XML sitemaps and the SEO of an international website
It’s no secret that businesses nowadays have customers from all over the world. Most businesses take the basic first step and translate their website into different languages. However, simple website translations are not enough. Having translated XML sitemaps can give businesses an extra edge over the competition.
Using an XML sitemap helps businesses with SEO and audience growth. Multilingual websites have pages in different languages; an XML sitemap for each means more indexed pages. It’s important to understand that improved indexing can influence search engine results and increase rankings. Therefore, using translated XML sitemaps is highly important and beneficial for websites.
The All-In-One SEO Plugin
The All In One (AIO) SEO plugin is one of the best SEO plugins that can be used with the WordPress content management system (CMS). It has advanced SEO modules, optimization features and can generate XML sitemaps.
Installing The AIO SEO Plugin
Activating the AIO SEO plugin and generating XML sitemaps
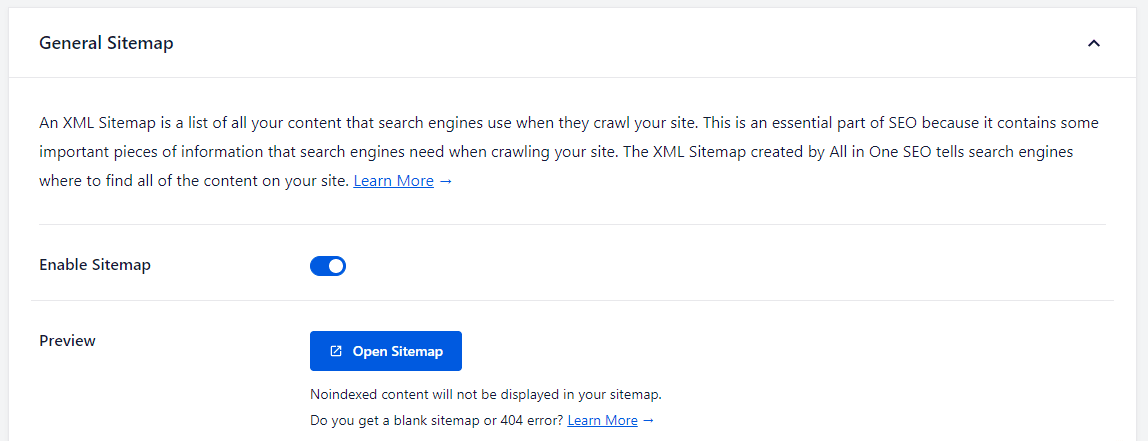
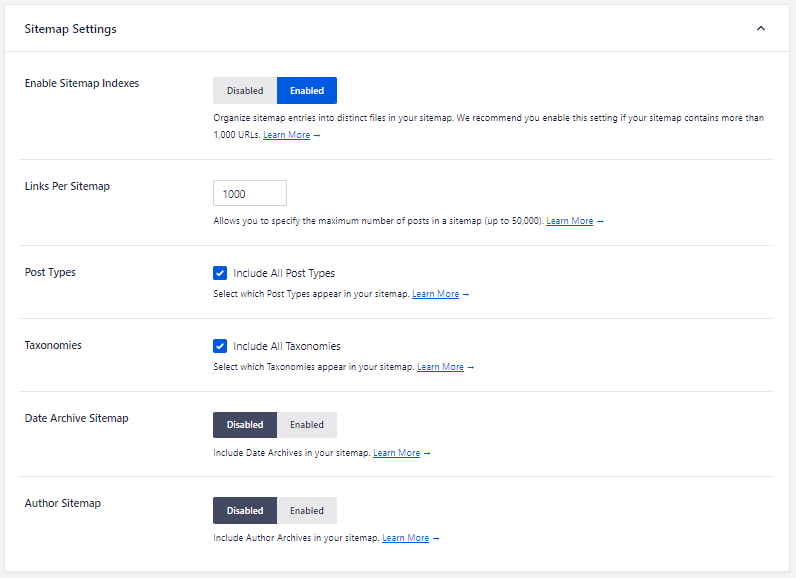
You can also scroll down the “Sitemaps Setting” tab and configure sitemap indexes, post types, links per sitemap, and more.
This will redirect you to a new page where you can see all your website’s sitemaps.
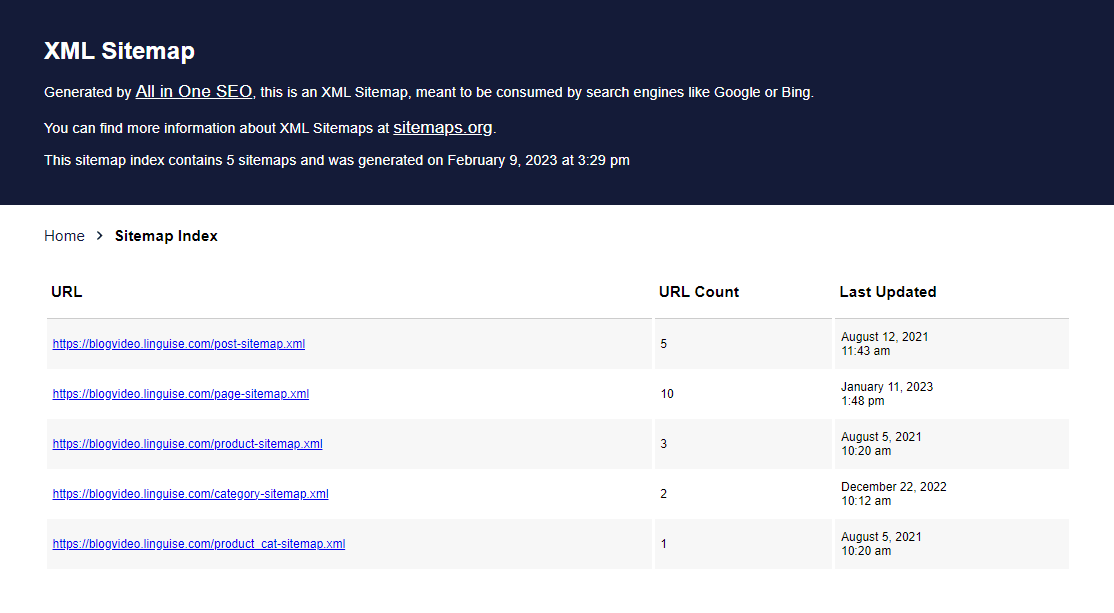
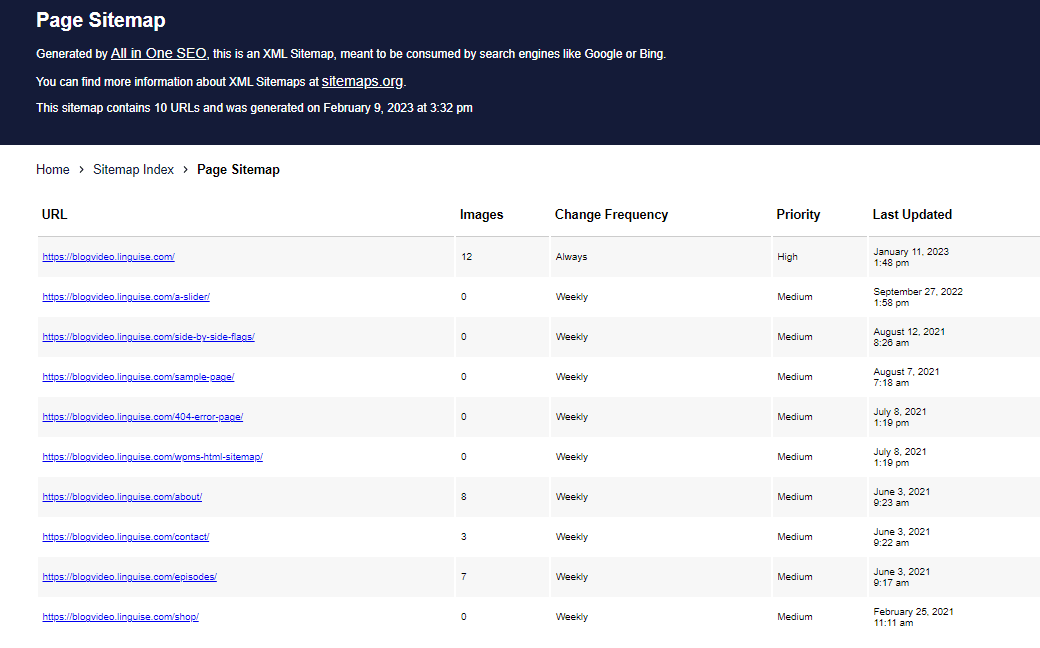
Translating the AIO SEO XML sitemaps
Most WordPress plugins require manual configuration for active custom post types translations. However, you can use Linguise to do all the translations for you automatically. Search for the Linguise plugin and install it to your CMS. The setup process will be completed within minutes.
Once the plugin is installed you must add the appropriate language tag to the URL. Let’s translate the “post-sitemaps.xml” file.
To do this, start by click-opening the file XML sitemaps file.
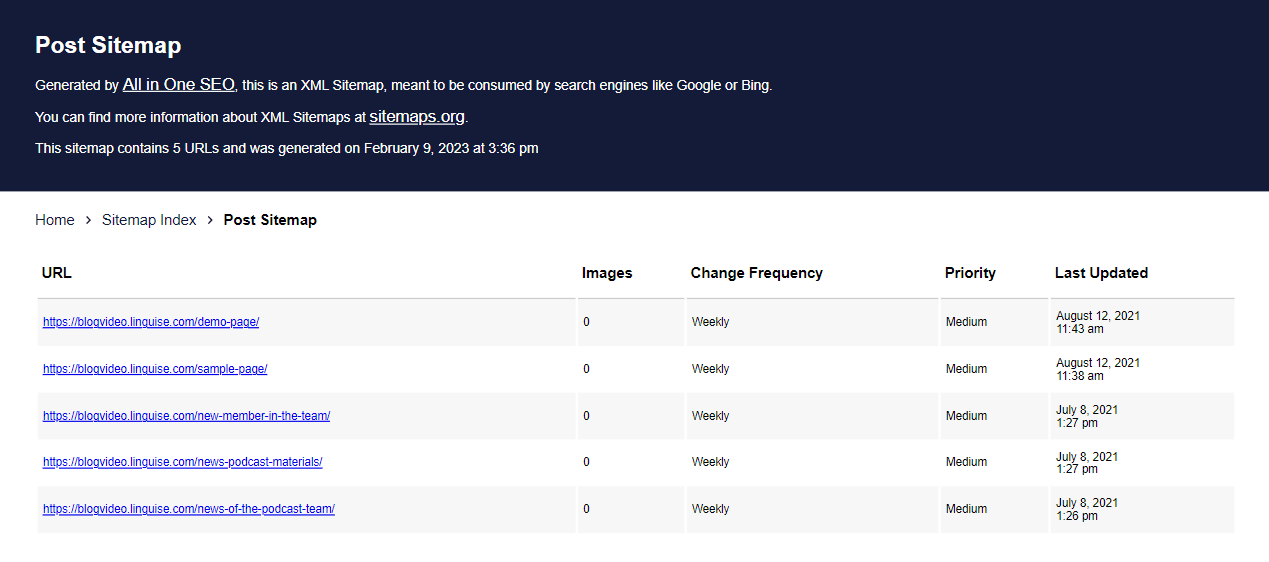
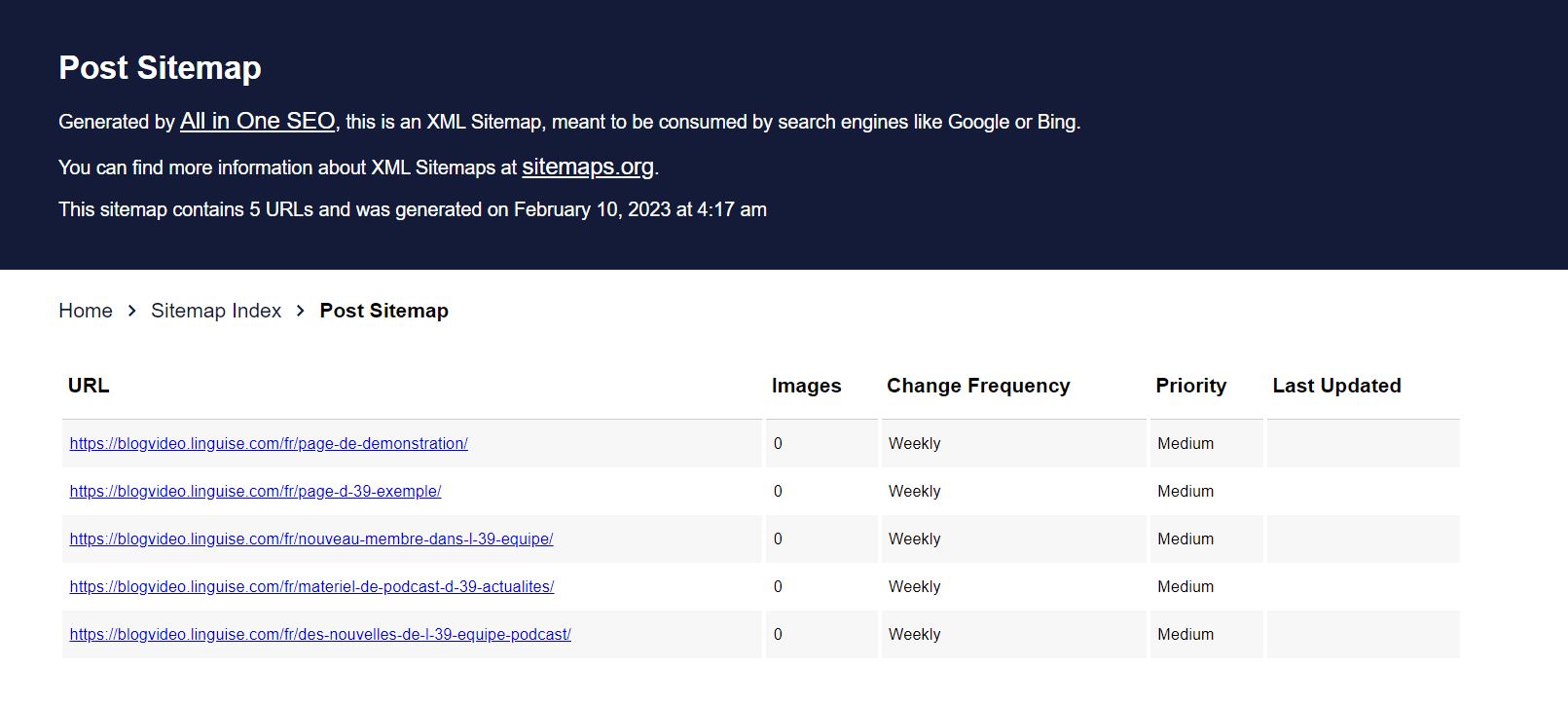
You can also check the translations by logging into your Linguise dashboard. You need to navigate to the domain section, add your website, and click the domain name of your website.


Finalizing translated XML sitemaps
Once your XML sitemaps are generated, you can submit them to popular search engines, including Google and Bing. However, you must ensure that all your website pages are included in the sitemap.
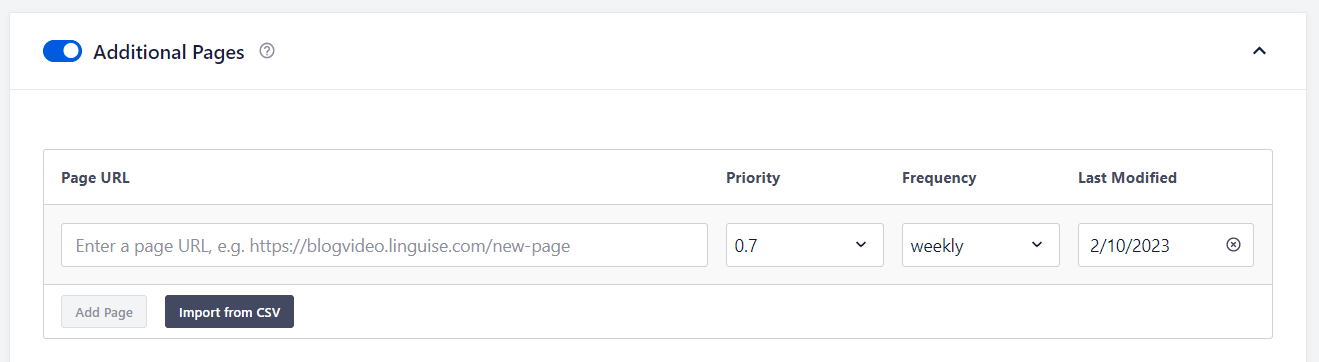
If you’re using an online store extension like WooCommerce, check to see if those pages are included in the XML sitemap. If they aren’t, navigate to the AIO SEO dashboard, then go to the “General Sitemap” section and enable “Additional Pages”. Now can manually add the URLs of your online store.
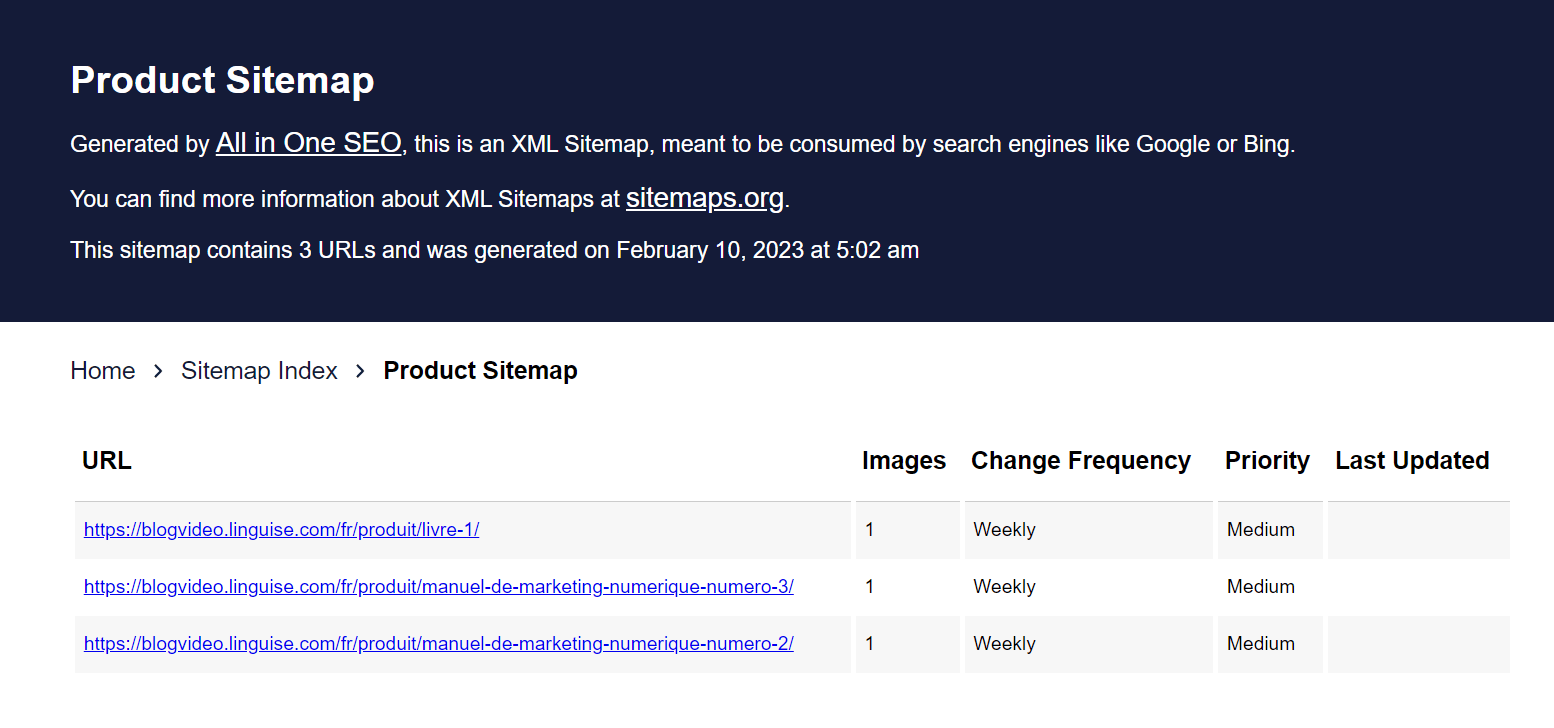
Submitting translated XML sitemaps to search engines
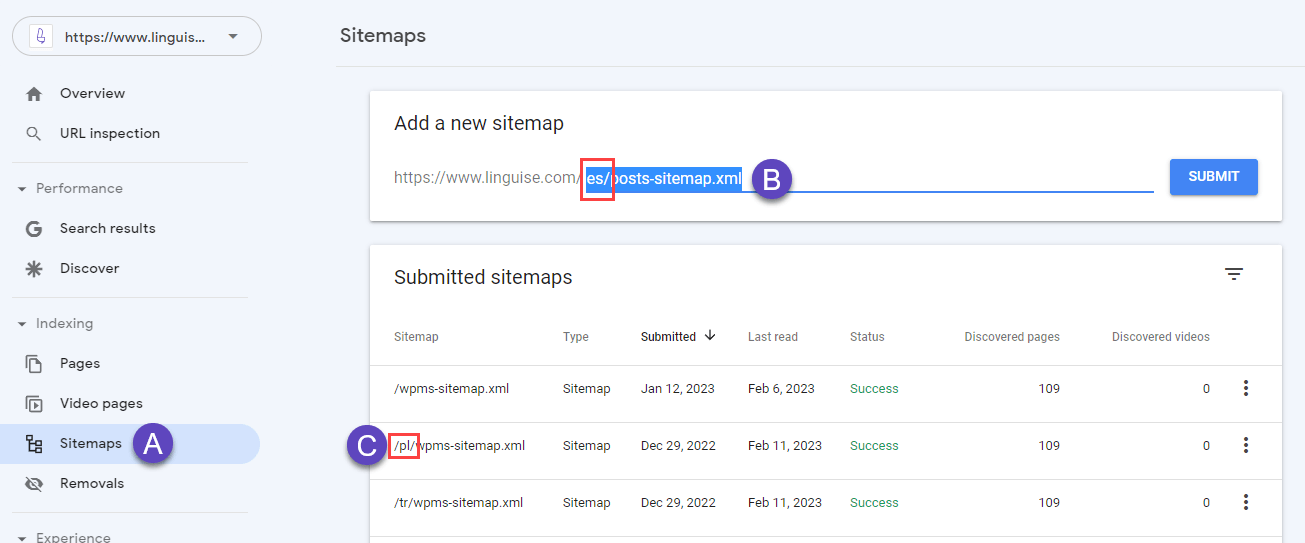
After you have finalized the translations for all the XML sitemaps, you can submit them to the search engine. Start by logging in to the search engine’s admin console and again navigate to the sitemap settings.
You must remove the previously existing sitemap files and then replace them with the new versions. The search engines will give you an indication of whether the files were read by crawlers. You can also check back after a week and see if the website pages have been indexed.
Key takeaways on sitemap translation
Online businesses often make countless SEO efforts to improve their visibility and become the customer’s first pick. However, not many of them focus on using translated XML sitemaps. These sitemaps are a list of all your website pages, and crawlers better understand the structure of your website and index all the pages. Using the AIO SEO plugin can help create translated XML sitemaps and can improve SEO and audience growth. Start using Linguise now and translate your website into multiple languages!




