Geotargeting vs. language targeting is crucial for businesses looking to expand their online reach. Both strategies help deliver personalized content, but they serve different purposes. Choosing the right approach depends on your business objectives, audience distribution, and SEO strategy.
This article explores the key differences, advantages, and considerations businesses should evaluate when deciding between geotargeting and language targeting to maximize engagement and conversions.
What is geotargeting?
Geotargeting is a strategy for displaying content based on a user’s geographic location. Businesses can customize users’ experiences based on their country, city, or zip code.
Geotargeting usually involves using IP addresses, GPS data, or location settings on a user’s device. Search engines like Google also support geotargeting with features like ccTLDs (country-specific domains) and region settings in Google Search Console.
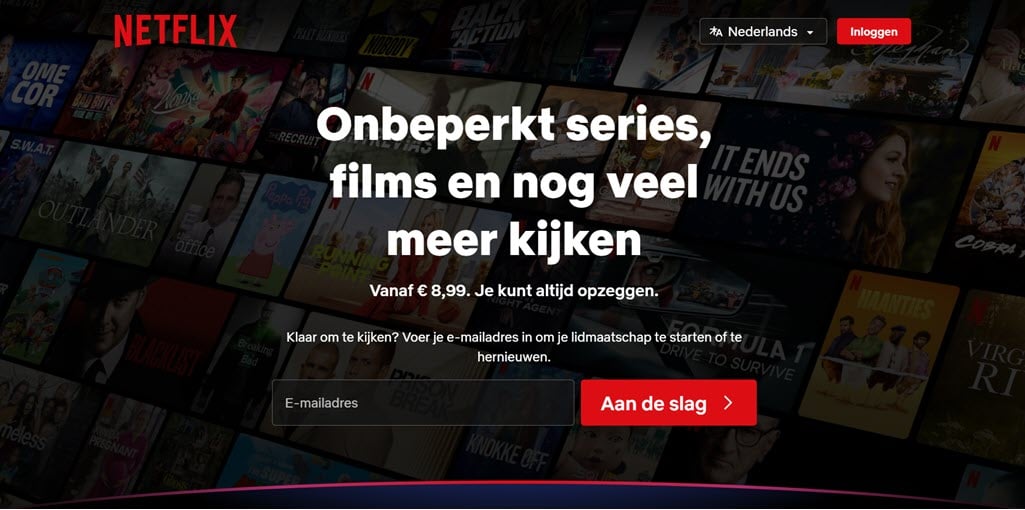
For example, Netflix is one business that has used this strategy. When a user located in France opens the Netflix page, it is automatically available in French with the domain address https://www.netflix.com/fr/.
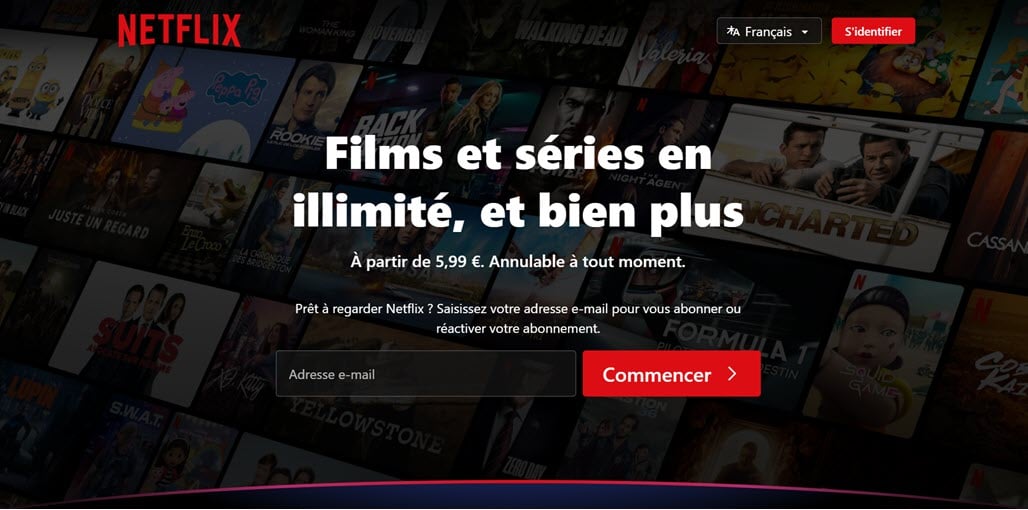
In addition, if the accessing user is located in the Netherlands, the page is displayed in Nederlands with the domain address https://www.netflix.com/nl.
What is language targeting?
Language targeting is the strategy of displaying content based on the language spoken by the user without considering their geographical location. This way, businesses can reach an audience that speaks a specific language, even if they are located in different countries.
This strategy is usually implemented using hreflang tags, which tell search engines which language version should be displayed to users. Some sites also offer a manual language selection feature so users can access content according to their preferences.
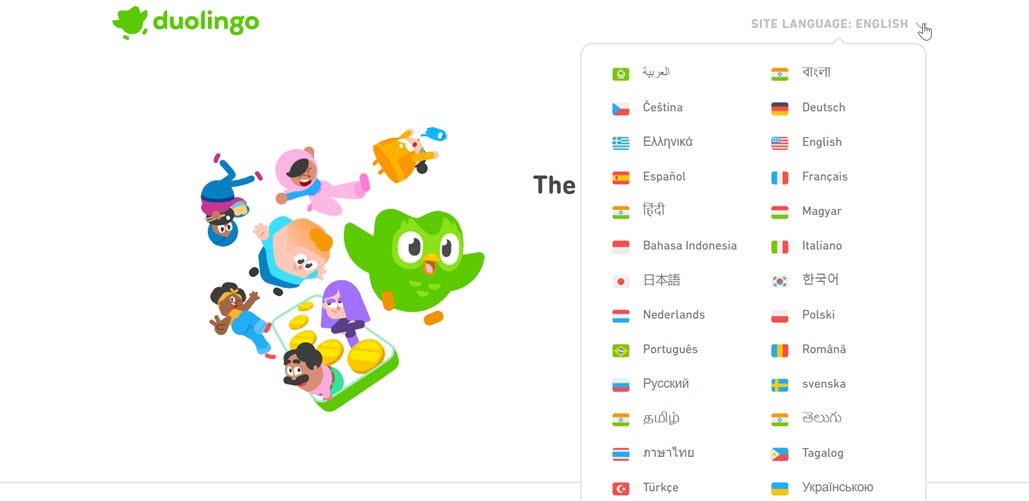
An example of language targeting can be seen on the Duolingo website. Whether users will access it from any location, the website will be available at the domain address https://www.duolingo.com/, and then, users can choose the language according to their preferences.
Key differences between geotargeting & language targeting
Businesses often use Geotargeting and language targeting to reach a global audience, but they have different approaches. Here are the differences between the two.
Purpose
Geotargeting aims to customize content, services, or products based on a user’s location. Businesses often use this strategy to provide a more relevant experience for audiences in a particular region, such as displaying local currency, appropriate payment methods, or country-specific promotions.
Language targeting, on the other hand, aims to serve content in a language that users understand, regardless of their location. This strategy is ideal for businesses with multilingual audiences in different countries, such as international news sites or tech companies wanting to reach global users with a more inclusive experience.
Implementation method

Geotargeting can be implemented through several methods, such as ccTLDs (country-code top-level domains), region-specific subdomains or subdirectories, and hreflang settings that include region codes. Businesses can also use tools like Google Search Console to target specific countries and customize location-based ads.
Meanwhile, language targeting relies more on hreflang tags to mark different language versions on the website. Businesses can also manually implement the language selection feature or use automatic detection based on the user’s browser settings. This way, users can access content in their preferred language more easily.
To support this, services like Linguise translation offer automatic implementation of hreflang and support ccTLDs for SEO optimization, so businesses can easily target users based on language without needing complicated manual configuration.
Impact on SEO

Geotargeting can help improve search rankings in specific countries but often reduces global visibility. For example, a site with a ccTLD domain, such as .co.uk is likely to be found more easily by users in the UK but may be suboptimal for searches outside the region. Therefore, this strategy is more effective for businesses that target local rather than global audiences.
On the other hand, language targeting allows businesses to reach audiences who speak the same language in different countries. With the proper use of hreflang, search engines can display pages in the appropriate language for users, improving their experience and reducing content duplication.
Potential challenges

One of the main challenges of geotargeting is the limited accessibility outside the targeted region. If not implemented properly, users from other countries may have difficulty accessing the needed content. In addition, this strategy can also increase operational costs due to the need to manage multiple site versions for different locations.
Meanwhile, language targeting faces challenges regarding translation accuracy and user experience. If content is automatically translated without validation, the results can be less accurate and reduce user trust. In addition, errors in hreflang implementation can cause search engines to display the wrong pages to users, negatively impacting SEO.
Best use case
Geotargeting is best suited for businesses that offer different services or products based on the user’s location. Examples are e-commerce that displays prices in local currency, restaurants that provide menus according to region, or streaming platforms that limit content based on country.
Language targeting, on the other hand, is ideal for businesses that have multilingual audiences without specific geographic restrictions. Examples include media companies, global organizations, or educational platforms that want to reach users with different language backgrounds.
From the above, here is a summary of the comparison table between Geotargeting vs. Language targeting based on various criteria:
Criteria | Geotargeting | Language targeting |
Purpose | Adjusts content, services, or products based on the user’s location. | Delivers content in the language understood by the user, regardless of their location. |
Implementation method | Uses ccTLD, location-based subdomains/subdirectories, or hreflang settings with a regional code. | Uses hreflang to mark language versions, manual language selection, or automatic detection based on browser settings. |
Impact on SEO | It improves rankings in a specific country but may reduce global visibility. | Allows broader reach for users who speak the same language across different countries. |
Potential challenges | It limits accessibility for users outside the target region and increases operational costs. | Risks inaccurate translations and hreflang misconfigurations, which can negatively affect SEO. |
Best use case | It is suitable for businesses offering different services or products based on location, such as e-commerce, restaurants, or streaming platforms. | This is ideal for businesses with a multilingual audience without geographical restrictions, such as media companies, global organizations, or educational platforms. |
Choosing between geotargeting vs. language targeting for your business
Deciding between geotargeting and language targeting depends on your business goals and audience needs. While geotargeting focuses on location-specific content, language targeting ensures users get information in their preferred language. Choosing the right approach requires evaluating several key factors.
Understand business goals

Your business objectives play a crucial role in determining the best strategy. Geotargeting is the better choice if you aim to offer region-specific products, services, or pricing. For example, an e-commerce store that wants to display local currency and shipping options would benefit from targeting users based on location.
On the other hand, if your main goal is to increase accessibility for multilingual audiences, language targeting is more effective. A global SaaS platform that wants to serve users across different countries without restricting access based on location should prioritize language-based content delivery.
Analyze the target audience

Understanding your audience’s location, language preferences, and behavior is essential. Geotargeting can improve engagement if most users come from specific regions and require localized content. For instance, a travel booking website might use geotargeting to show deals and promotions relevant to users in different countries.
However, language targeting is more suitable if your audience is multilingual but not tied to a specific region. A global news website that serves readers in multiple languages should prioritize translating content instead of restricting it by location.
Consider SEO and visibility
SEO plays a vital role in reaching the right audience. Geotargeting can improve rankings in specific countries but may limit global search visibility. A website with a country-specific domain (.uk, .fr, .de) is likely to rank well in those countries but might not perform as well in global searches.
Language targeting, on the other hand, can enhance visibility across multiple regions by ensuring content is available in different languages. A website using hreflang tags to provide content in Spanish, French, and German can attract international traffic, regardless of location.
You can use an automated solution like Linguise, which also considers SEO on multilingual sites. It automatically implements hreflang and ccTLDs to ensure that search engines index each language version correctly. With Linguise, implementing hreflang tags becomes more efficient without adding code manually, thus minimizing the risk of misconfigurations that could affect SEO.
Evaluate infrastructure and costs

The technical and financial investment required for each strategy varies. Geotargeting often involves managing multiple website versions, which can increase maintenance costs. Businesses using country-specific domains or subdirectories must allocate resources for content updates, hosting, and SEO for each location.
Language targeting, while less complex regarding infrastructure, requires high-quality translations. Investing in human or machine translation services ensures accuracy and a better user experience. However, poor translations can negatively impact credibility and engagement.
Conclusion
Geotargeting vs. language targeting is important for businesses looking to expand their global reach. Language targeting is a more flexible option to serve content in multiple languages without restricting access based on location. On the other hand, if your business offers different services or products in each country, geotargeting is more effective for customizing the user experience.
For easy implementation, try Linguise and create an account now to optimize your multilingual SEO strategy with automatic hreflang and ccTLD support. With Linguise, businesses can ensure each language version of the website is indexed correctly without requiring complex manual configuration.