Entering international markets feels like embarking on an exciting new adventure—filled with various possibilities and, of course, significant challenges. We understand the thrill of reaching new customers and the importance of taking the right strategic steps. Whether you’re just beginning to dream big or are already on the path to global success, understanding the best strategies for entering foreign markets can be a game changer.
A study published by the Institute for International Economics concluded that U.S. companies that export grow faster and are also 8.5% less likely to go out of business than non-exporting companies. This is just one example of the significant impact of entering international markets.
So, what do you think? Are you interested in trying it as well? If so, let’s explore some entry strategies for international markets together and discuss them!
Why should you enter foreign markets & benefits for your business?

Entering foreign markets is about more than expanding your business reach; it’s about unlocking doors to unlimited opportunities.
Why go international? It’s simple, growth and resilience. No matter how large, domestic markets have limits. However, entering foreign markets opens you up to a much broader and more diverse customer base. It’s not just about boosting sales but also about minimizing risk by diversifying your revenue streams.
Here’s some data that highlights the importance of international expansion.
- According to a report from the World Trade Organization, global trade reached $25 trillion, with merchandise and services exports totalling $19 trillion and $6 trillion, respectively.
- Small business exports significantly contribute to the U.S. economy; in 2017, exports generated $541 billion in output and supported over 6 million jobs.
These figures show that entering international markets, like through exports, can yield incredible business profits. The benefits you will gain by entering foreign markets include risk diversification, accessing global talent, increasing competitiveness, extending product life cycles, increasing brand value. While entering foreign markets certainly has its challenges, the benefits far outweigh the risks, transforming your business from a local player to a global force and opening the door to sustainable growth and long-term success.
10+ foreign market entry strategies

Before we discuss the strategies for entering foreign markets in detail, let’s remember that every business is unique, with its own set of needs and challenges. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution in the global business world. Choose the strategy that best aligns with your goals, resources, and the characteristics of your target market.
#1 Direct exporting
Direct exporting is a strategy where your company sells products or services directly to customers in another country, often through local distributors or agents. This approach gives you complete control over the marketing and sales process, allowing you to build direct relationships with foreign customers.
For example, the Indonesian fashion company Batik Keris has successfully exported its batik products to Southeast Asia and Europe countries. They have partnered with local distributors in each destination country while maintaining control over branding and product quality.
Pros:
- Full control over marketing strategy and pricing
- Direct relationships with customers
- Potential for higher profit margins
Cons:
- Requires significant initial investment
- Higher risk due to limited knowledge of the local market
- Challenges in managing international logistics and regulations
#2 Licensing
Licensing involves granting a local company the right to use your trademarks, patents, or other intellectual property in exchange for royalties. This strategy allows you to enter foreign markets with lower financial risk.
A successful example of this strategy is Aqua, an Indonesian bottled water brand, which licensed its technology and brand to the Danone Group. This partnership enabled Aqua to expand its global reach while maintaining a dominant position in the Indonesian market.
The following image comes from the AQUA website and shows what has happened with Danone. As part of Danone, AQUA gets access to the latest technology and global marketing strategies. At the same time, Danone expands its portfolio in the beverage market by strengthening its presence in various regions.
Pros:
- Lower costs and risks for entering new markets
- Leverages the knowledge and network of local partners
- Potential for passive income through royalties
Cons:
- Limited control over operations and product quality
- Risk of intellectual property infringement
- Potential to create future competitors
#3 Greenfield investment
Greenfield investment is a strategy where a company builds its business operations from the ground up in the target country. This involves significant investment in constructing production facilities, offices, or other infrastructure.
For example, Toyota built a car manufacturing plant in Indonesia in the 1970s. They started from scratch, building production facilities, training the local workforce, and developing the supply chain.
Pros:
- Full control over operations and strategy
- Potential for significant long-term profits
- Ability to leverage local government incentives
Cons:
- Very large initial investment
- High risk related to market and regulatory uncertainties
- It takes a long time to reach the break-even point
#4 E-commerce and digital expansion
This strategy involves using e-commerce platforms and digital technology to enter foreign markets without a significant physical presence.
For example, Shopee has used this strategy to expand its reach into other Southeast Asian markets through partnerships with regional platforms and optimization for cross-border searches.
The following is an example of a Shopee company that has succeeded in spreading its wings not only in Singapore but also to several countries in Southeast Asia, such as the Philippines. That’s why they also create web pages in the Filipino language and currency.
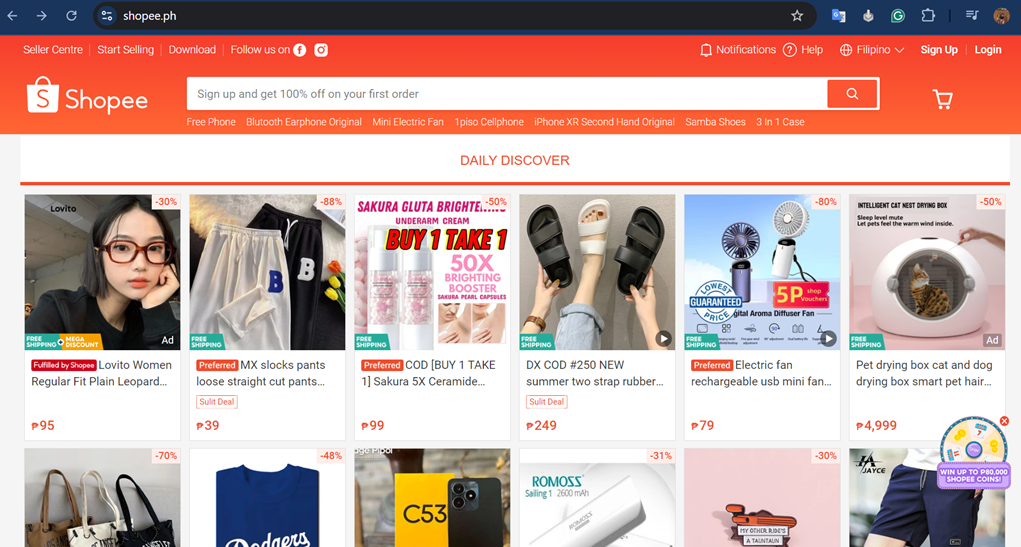
Pros:
- Relatively low market entry costs
- Ability to reach global consumers quickly
- Flexibility in adapting strategies
Cons:
- Challenges in building consumer trust without a physical presence
- Complexity in cross-border logistics
- Intense competition in the digital space
#5 Turnkey projects
In this strategy, a company provides a complete, ready-to-use solution to clients in the target country, including design, construction, and initial operations.
For example, the Saudi Arabian oil company Saudi Aramco partnered with the American-Irish oil services company Weatherford International to acquire drilling and intervention services. In this turnkey project, Weatherford was responsible for planning and executing all operations on behalf of Saudi Aramco and delivering 45 wells per year to them.
Pros:
- Potential for significant revenue from large-scale projects
- Builds international reputation
- Facilitates technology and knowledge transfer
Cons:
- High risk associated with completing projects on time and within budget
- Complexity in managing local regulations and workforce
- Dependence on the political and economic stability of the target country
#6 Contract manufacturing
In this strategy, a company manufactures goods based on specifications provided by another brand.
For example, many companies in Indonesia produce clothing for global brands like Nike, Adidas, and H&M.
Pros:
- Low market entry costs
- Leverage existing production expertise
- Opportunity to learn from international standards
Cons:
- Lower profit margins
- Lack of control over branding and marketing
- Risk of dependency on a few large customers
#7 Piggybacking
Piggybacking involves partnering with an established company in the target market to leverage its distribution network and market knowledge.
For example, the Swiss chocolate company Lindt & Sprüngli partnered with Hershey’s to enter the U.S. market. Lindt used Hershey’s extensive distribution network and local market expertise to expand its reach in this highly competitive market.
Pros:
- Quick access to new markets with lower risk
- Leverage the reputation and network of the partner
- Rapid market learning
Cons:
- Dependence on the partner for success
- Potential conflicts of interest if products compete
- Limited control over marketing and distribution strategies
Each of these strategies has its advantages and disadvantages. The right strategy choice should consider various factors, such as company resources, product characteristics, target market dynamics, and the company’s long-term goals.
#8 Joint ventures
A joint venture is a strategic partnership in which two or more companies create a new entity that they jointly own. This collaboration enables the sharing of resources, risks, and profits while working towards shared business objectives.
For example, BMW and Brilliance Auto Group. Due to local regulations in force at the time, BMW needed a partner from China to produce cars in that country. Therefore, BMW collaborated with Brilliance Auto Group to build BMW Brilliance. This collaboration allowed both companies to access new markets that could not be reached individually: BMW gained access to the Chinese market. At the same time, Brilliance Auto Group was able to enter the luxury car market.
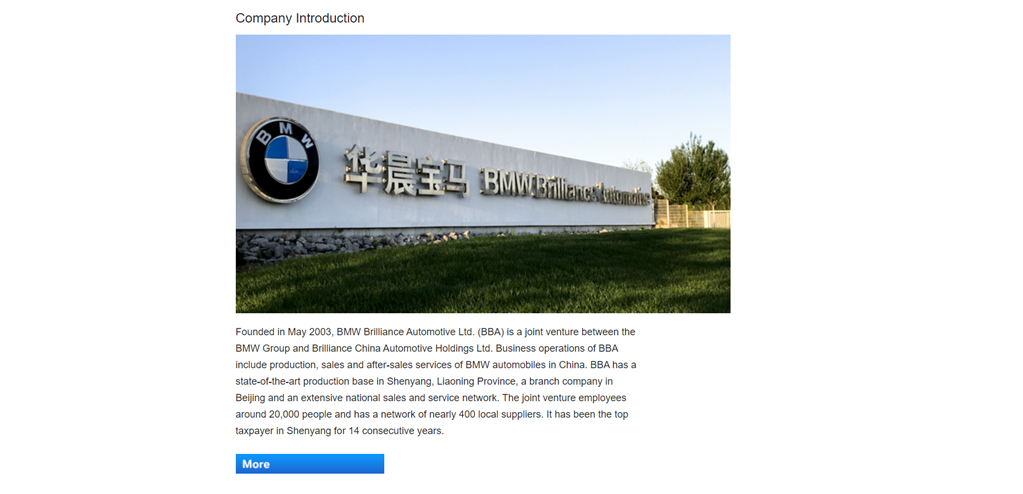
Pros:
- Shared investment and risk
- Access to the partner’s local market knowledge and resources
- Combined expertise and capabilities
Cons:
- Potential for conflicts between partners
- Shared control can lead to slower decision-making
- Complexity in managing and aligning interests
#9 Strategic alliances
Strategic alliances involve partnerships between companies to achieve specific objectives while remaining independent. This can include collaborations on marketing, technology, or product development.
For example, a global car manufacturer might ally with a technology company to develop advanced in-car infotainment systems.
Pros:
- Flexibility in the collaboration terms
- Access to complementary resources and expertise
- Enhanced innovation through shared knowledge
Cons:
- Risk of misalignment in goals and priorities
- Limited control over the alliance’s operations
- Potential for disputes over intellectual property and profits
#10 Acquisition
Acquisition involves one company purchasing another company to gain control over its assets, technology, or market presence. This strategy allows for quick market entry or expansion.
For example, a large retail chain might acquire a smaller regional competitor to increase its market share and expand its geographic reach.
Pros:
- Immediate access to new markets and resources
- Enhanced market presence and competitive advantage
- Potential for increased revenue and market share
Cons:
- High costs associated with the acquisition
- Integration challenges and potential cultural clashes
- Risk of overestimating the target company’s value
#11 Franchising
Franchising allows a company to expand its brand and operations by granting others the right to use its established business model and intellectual property.
Consider a successful fast-food chain, like McDonald’s, that wants to grow its presence globally. Instead of building and managing new outlets directly, McDonald’s can offer franchise opportunities to local entrepreneurs. These franchisees run their own McDonald’s restaurants, adhering to the company’s established standards while benefiting from the brand’s recognition and support systems. One of them is the McDonalds franchise in Indonesia.
Pros:
- Quick growth into new markets with lower financial risk for the franchisor.
- Franchisees benefit from operating under a recognized and trusted brand.
- Comprehensive support and training for franchisees help maintain operational consistency.
Cons:
- Less direct control over franchise locations can impact brand consistency.
- Royalties and fees reduce profitability for both franchisor and franchisee.
- Franchisees rely on the franchisor for support and adherence to system standards, limiting flexibility.
Factors to consider when entry strategies for international markets
Several key factors must be carefully considered to ensure a successful expansion when planning to enter international markets. Let’s explore some of the most critical aspects you need to evaluate.
Market Conditions
When planning international expansion, it’s crucial to understand the market conditions in the target country. This includes analyzing market size, growth potential, and the demographic and economic trends that influence it. Additionally, the intensity of competition should be carefully considered. Mapping the competitive landscape and identifying your company’s unique advantages will help establish a strong strategic position. Infrastructure and supply chains must also be assessed to ensure your business can operate smoothly in the new market.
Goals
Setting clear short-term and long-term goals is essential for international expansion. You must align your market entry strategy with the company’s vision while considering stakeholder expectations and available resources. Also, consider whether your focus will be on market penetration with existing products or diversification with new products. Establishing clear milestones and regularly assessing progress will ensure your strategy remains on track.
Cultural Differences
Cultural differences are a critical factor in international expansion. Social values, traditions, and local cultural norms often influence consumer preferences and purchasing behavior. To succeed, it’s important to understand these cultural nuances and adapt your marketing and business operations accordingly. Investing in ethnographic research and cross-cultural training can help avoid misunderstandings and build strong relationships with local consumers.
Legal and Regulatory Environment
Understanding the legal and regulatory environment in the target country is crucial before starting expansion. This includes grasping the new market’s trade and investment policies and intellectual property protections. Ensuring compliance with local laws is crucial to avoid potential legal issues. Consulting with local legal and tax experts effectively ensures your business adheres to all applicable regulations.
Language Barriers
Language differences can pose major obstacles to international expansion. Effective communication with customers and business partners is critical, often requiring investment in translation services and adaptation of marketing materials to the local cultural context. Ensure accuracy and cultural appropriateness in all written materials through localization services. That’s why creating a multi-language website can help overcome language barriers in your business
Overcome language barriers when entering foreign market

One solution to address language barriers in international expansion is to use automatic translation services that can quickly and efficiently translate and localize business content. One reliable platform for this is Linguise.
Linguise offers high-quality automatic translation, using AI and neural technology to handle various languages and cultural nuances. Linguise ensures that your content is accurately translated and adapted to the local cultural context, ensuring your message remains relevant and practical across different markets. Features of Linguise include.
- Live editor for localization – Allows real-time editing of translations directly on the web page. Kolaborasi dengan professional translators.
- Multilingual SEO implementation – Optimizes content for search engines in multiple target languages.
- Automatic visitor language detection – Presents content automatically in the visitor’s preferred language.
- Translation exclusion – feature to load your website content based on words, lines, pages, or others. This is possible if there are special words or terms you don’t want to translate into another language because you fear it will confuse the reader.
Several elements need to be localized in the website localization process.
- Content text
- Images and layout design
- Currency and number formats
- Date and time formats
- Contact information and addresses
- Forms and input fields
- Culturally sensitive design elements
It’s important to note that various businesses can benefit from website translation for global expansion. For more information on the types of businesses that should consider translating their websites, you can visit a guide on business websites that need website translation.
Conclusion
Entry strategies for international markets are crucial for businesses looking to expand their reach and tap into global opportunities. As we’ve explored, there are numerous approaches to entering foreign markets, each with its advantages and challenges. From direct exporting to e-commerce expansion, the key is to carefully assess your company’s goals, resources, and target market conditions to select the most appropriate strategy.
Regardless of your chosen entry strategy, overcoming language barriers is essential for effective communication with your new audience. Tools like Linguise can play a vital role in this process, offering high-quality automatic translation and localization services to ensure your message resonates across linguistic and cultural boundaries. To start leveraging these benefits for your international expansion, consider creating a Linguise account today and take the first step toward entering global markets.