Google is still the most widely used search engine in the world. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t other search engines. Baidu, the Chinese search engine giant, offers a unique alternative, especially for those targeting the Chinese market. While Google dominates the global scene, Baidu significantly influences China, the world’s most populous country.
This article will discuss the key differences between Baidu and Google. Start with an overview of Baidu and Google and an SEO comparison. Let’s start!
Overview of Baidu vs Google
Before discussing Baidu and Google, we will briefly discuss what Baidu and Google are.
What is Baidu?

Baidu, often called the “Google of China,” is a dominant search engine in the Chinese market. Baidu search engine holds 52.86% of the market share. Founded in 2000 by Robin Li and Eric Xu, Baidu has grown into a multifaceted technology company offering services tailored to Chinese users, including search, maps, cloud storage, and more. Its deep understanding of the Chinese language, culture, and regulatory environment has solidified its position as the go-to search engine for over a billion users.
Beyond the basics, Baidu offers.
- Baidu Tieba: A popular online community forum where users discuss various topics, fostering a unique social network experience.
- iQiyi: A streaming service similar to Netflix, providing a vast library of movies, TV shows, and original content.
- Baidu AI and Big Data Solutions: Through its Apollo project, Baidu has invested heavily in artificial intelligence and offers AI tools like facial recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving technology.
Baidu’s ecosystem reflects China’s digital landscape, which has its regulations, user preferences, and technology standards. For businesses looking to engage Chinese audiences, Baidu’s tools provide valuable avenues for digital marketing.
What is Google?

Google is a search engine. Two Stanford University students founded Google, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, in 1998. Initially, they created Google as a research project, but over time, Google developed into the largest technology company in the world.
Google is currently used by 8.5 billion users worldwide every day.
- Gmail: A top-rated free email service.
- Google Maps: Highly detailed and accurate online maps.
- YouTube: The world’s largest video-sharing site.
- Google Drive: Online file storage service.
- Google Docs: Online word processing, spreadsheet, and presentation application.
What are the key similarities Baidu vs Google?
Before discussing the differences between Baidu and Google, you need to know that there are similarities between these two search engines. Here are some of them.
1. Content relevance and freshness

Both Baidu and Google prioritize content relevance as a critical ranking factor. Baidu’s white paper emphasizes that meeting user needs through high-quality content is essential. Both search engines evaluate page quality based on content integrity, aesthetics, user-friendliness, and source authority. While their specific algorithms differ, both platforms reward content that aligns with user intent and maintains high editorial standards. Both search engines value fresh and regularly updated content, though they may weigh this factor differently in their ranking algorithms.
2. User experience and engagement
Both search engines emphasize user experience as a core ranking factor. They prioritize sites that offer smooth, engaging, and user-friendly experiences. Key aspects valued by both platforms include page speed, intuitive layout, and high-quality, relevant content. While their specific metrics may differ – with Google focusing on Core Web Vitals and Baidu emphasizing its Lightning Algorithm – both ultimately aim to reward sites that provide exceptional user experiences.
3. Mobile-first indexing
Both search engines have fully embraced mobile-first indexing, reflecting the growing importance of mobile search. Key priorities for both platforms include speed, load time, image optimization, and handling of dynamic elements. Both require that mobile sites contain high-quality, valuable content available on desktop versions, including crawlable and indexable text, video, and images. However, both platforms acknowledge that mobile and desktop rankings may differ due to device-specific ranking factors.
4. Artificial intelligence integration
Both Baidu and Google have developed powerful AI language models to enhance their search capabilities:
- Baidu ERNIE: This AI model is designed to understand and generate human language in a comprehensive and contextually relevant manner. It can handle complex language nuances, generate creative text, and translate languages.
- Google BERT: A similar AI model developed by Google, BERT helps the search engine better understand the context and intent behind search queries. It can understand complex sentences and provide more relevant search results.
Both ERNIE and BERT are significant advancements in AI, enabling more accurate and relevant search results. They demonstrate the increasing role of AI in shaping the future of search and language technology.
Key differences between Baidu vs Google
After learning the definitions of the two search engines above, we will discuss several things that distinguish Baidu from Google.
Market focus and language
As of August 2024, Google dominates the global search engine market with a 90.48% share, while Baidu holds only 0.79%. This stark difference reflects their different market focuses—Google is global and multilingual, while Baidu focuses almost exclusively on the Chinese market. Baidu optimizes its search engine for Mandarin, and nearly all its content is in Chinese.
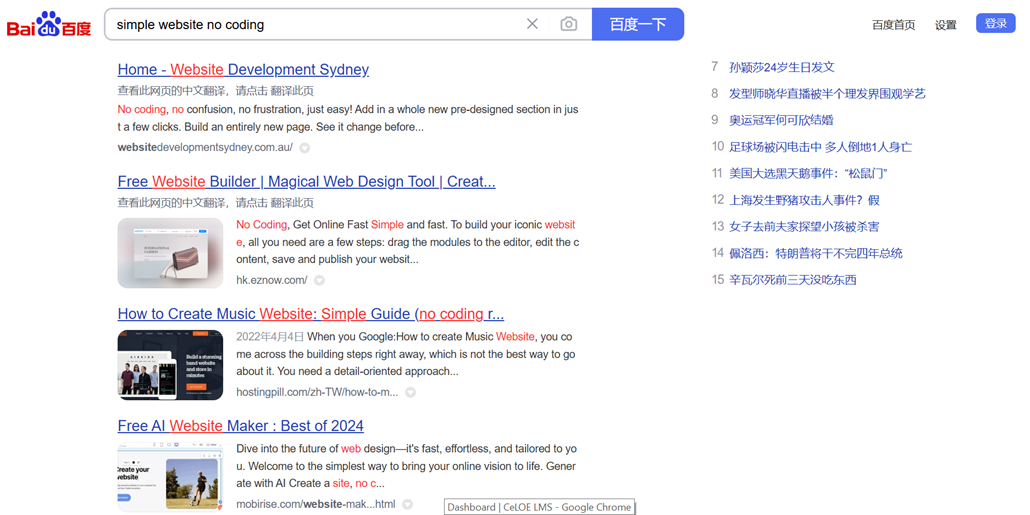
Baidu is the top choice in mainland China, and it commands about 75% of the domestic search market. You can still enter keywords other than Chinese, as in the following example. The content will appear in English, but for navigation, etc. Baidu still uses Chinese.
Government regulations and censorship
Baidu operates under the strict supervision of the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC), requiring it to comply with complex regulations. According to China’s updated Cybersecurity Law in 2021, Baidu must store all user data on local servers and be asked to share it with the government on time.
Due to these regulations, Google faced a major dilemma in 2010 when the Chinese government requested access to Gmail user data and demanded stricter censorship. This led Google to relocate its operations to Hong Kong. This difference in approach has significant business implications: Baidu enjoys dominance in China’s domestic market with government support, while Google’s services, including Search, Gmail, Drive, and YouTube, have been blocked in China since 2010. Although Google attempted to re-enter China in 2018 with the censored Dragonfly project, it was canceled following heavy criticism from Google employees and human rights activists.
The impact of these regulatory differences is also evident in the user experience. Baidu users cannot access information on sensitive topics, such as the 1989 Tiananmen events or the situation in Tibet. Google users have more comprehensive access to information, except for content that violates local laws in each country.
Paid advertising and features
Baidu places a greater emphasis on paid advertising in search results, with ad formats that can occupy more space on the page than Google. They offer unique features like Brand Zone, providing high visibility for advertisers and for example searching keyword 耐克 (Nike).
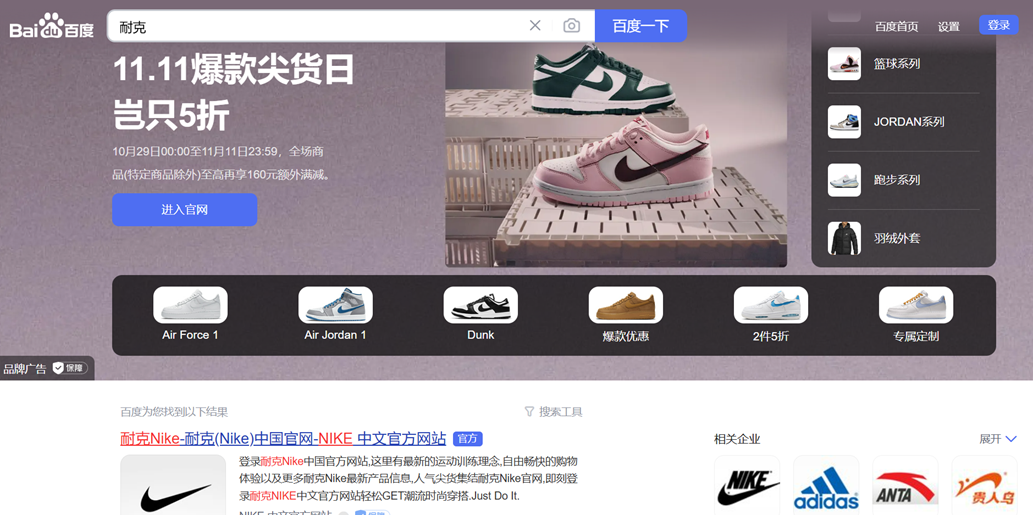
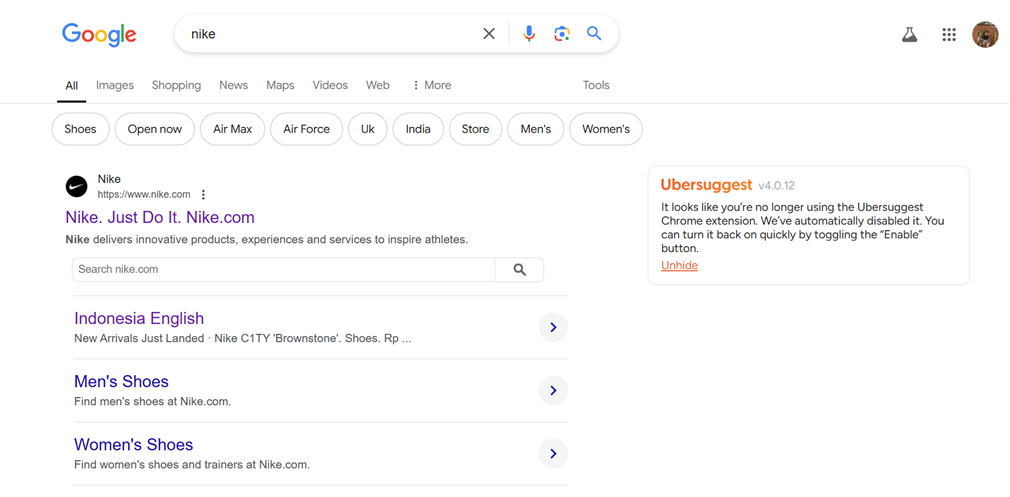
In contrast, Google maintains a stricter balance between organic results and paid ads. Although Google Ads is a major revenue source, its ads are more subtly integrated with organic search results. For instance, the example below illustrates this balance.
Content and service integration
Baidu integrates its services with China’s vast digital ecosystem, including Baidu Tieba (discussion forum), Baidu Maps, and cloud services. It also has strong integration with popular social and e-commerce apps in China.
In addition, Google also offers integration with its global services, such as Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Drive. This approach reflects a more universal strategy that is not focused on one market.
7 key comparison of SEO & ranking factors between Baidu vs Google
After exploring some differences between Baidu and Google, let’s examine their distinctions in terms of SEO and ranking factors.
1. Backlink and authority
Baidu values backlinks from Chinese-based websites, especially those with .cn or .com.cn domains, considering these more impactful. Google uses a more sophisticated backlink evaluation system through PageRank and domain authority metrics, assigning value based on the relevance and authority of the linking site, regardless of its geographic location. Baidu is more vulnerable to link spam manipulation, though it imposes heavy penalties when detected, with recovery sometimes taking years.
2. Page load speed and technical SEO
Baidu has a low tolerance for slow loading, with an ideal load time of under 2 seconds for the first contentful paint (FCP). Sites hosted in China experience an advantage, loading up to 200% faster than international hosting. Google, meanwhile, uses Core Web Vitals, assessing LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), FID (First Input Delay), and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift), with sites that meet these standards more likely to rank well. Baidu struggles with JavaScript and AJAX crawling, while Google effectively handles modern web technologies, including SPAs and PWAs.
3. Local SEO focus
Baidu highly prioritized local Chinese content, with 95% of top search results from China-based websites favoring sites with an ICP (Internet Content Provider) license and verified physical addresses in China.
Google, in contrast, uses a flexible local approach, identifying local relevance based on user location, language, and search context, valuing Google My Business listings and local reviews.
4. Indexing and content speed

Baidu’s indexing and ranking algorithms emphasize hosting location and ICP (Internet Content Provider) compliance, prioritizing sites with faster load times and stable connections within China. Locally hosted sites with an ICP license are typically crawled and indexed more frequently, improving their visibility and ranking on Baidu. This preference shows Baidu’s focus on providing Chinese users with fast, reliable access to content without latency from overseas hosting.
In contrast, Google’s algorithms assess a wide range of factors, such as mobile-friendliness, HTTPS security, and content relevance, with site speed as one of the key ranking factors. However, Google does not impose specific hosting location preferences, aiming to deliver a consistent user experience globally. Google emphasizes content quality and relevance to meet user intent worldwide, focusing on metrics like bounce rate, dwell time, and other engagement signals. This priority difference underscores the need for distinct SEO strategies for each platform.
5. Speed index update
Baidu has a slower index update cycle, which is about once a week. New sites generally undergo an evaluation period of up to three months before fully indexing.
Meanwhile, Google has a more dynamic and fast indexing system, capable of indexing new content within hours to days. This makes Google more responsive to real-time content and site updates.
6. Algorithm updates and frequency

Google frequently updates its SEO algorithms, with an average of 500-600 small changes and a few major updates each year, typically aimed at improving search quality and user experience. Baidu’s updates are less frequent and focused mainly on adapting to Chinese government regulations and local user preferences. While Google is transparent with major updates and offers guidance to webmasters, Baidu is more reserved in communicating algorithm changes.
7. Webmaster tools
Both Baidu and Google provide webmaster tools, but they have different functionalities. Baidu Webmaster Tools offers sitemap submission, index monitoring, and keyword analysis. Google Search Console (GSC) is more comprehensive, offering real-time ranking reports, site health analysis, and specific SEO improvement recommendations. Though Baidu’s tools are not as extensive, they provide valuable insights into how Baidu indexes content, helping optimize SEO strategy and improve visibility and ranking on Baidu’s SERP.
Conclusion
Now you know the differences between Baidu and Google regarding key differences and SEO. If you are interested in optimizing your website on Baidu’s search engine, prepare to translate your website content into Chinese to be more easily indexed on their search engine.
One of the automatic website translation tools you can rely on to translate automatically is Linguise. It provides more than 85 languages, including Mandarin, both simplified and traditional. What are you waiting for? Create your Linguise account and increase traffic from Baidu!